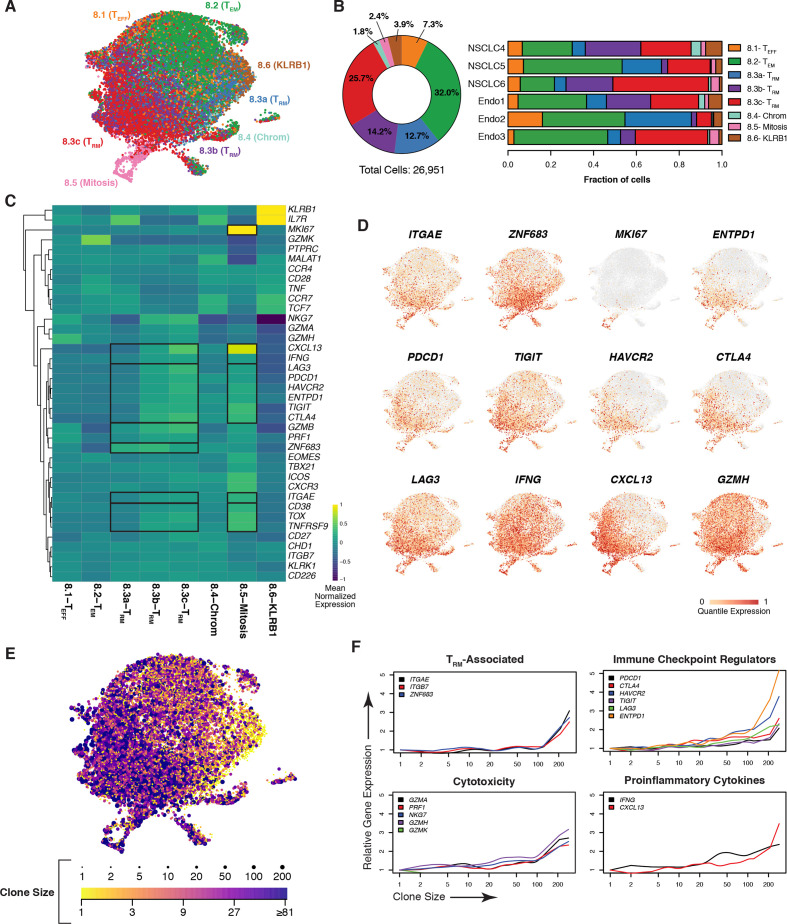
Figure 3.
Tumor CD8 +TRM cells are clonally expanded and express genes associated with cytotoxicity and dysfunction. (A) UMAP of CD8+ T cells from NSCLC (n=3) and endometrial (n=3) tumor samples with clusters colored by subset identity as analyzed by scRNAseq. (B) Frequency of each CD8+ T-cell cluster among all tumors assessed with samples in aggregate (left) or by individual (right). (C) Heatmap depicting relative expression of T cell-associated genes, with a dendogram indicating results of hierarchical unsupervised clustering (left), across CD8+ clusters. Genes are globally scaled with an expression range from −1 (dark blue) to 1 (yellow). (D) UMAP overlay of genes associated with the TRM phenotype, proliferation, dysfunction, as well as genes correlated with ITGAE in the bulk RNAseq and heatmap analyses. Individual cells are colored on a scale of gray (0) to red (1) according to the quantile of their expression. (E) Extent of clonal expansion, as determined by scTCRseq, for each cell overlaid onto the UMAP (A). The breadth of TCR clonality is represented by dot size and by color, ranging from a clone size of 1 (yellow) to greater than 81 (purple). (F) Expression of indicated genes (y-axes) as a function of the size of a given clonotype (with clone size rank ordered on the x-axis) for resident memory T-cell phenotype, checkpoint regulator, cytotoxicity, and proinflammatory cytokine genes. NSCLC, non-small cell lung cancer; RNAseq, RNA sequencing; scRNAseq, single-cell RNA sequencing; scTCRseq, single-cell TCR sequencing; TCR, T-cell receptor; TRM, tissue-resident memory T; UMAP, uniform manifold approximation and projection.