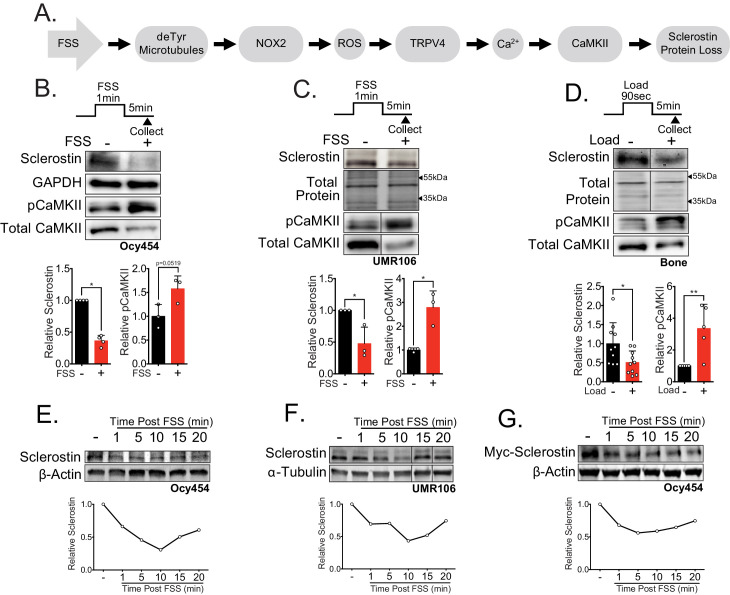
Figure 1. Sclerostin protein is rapidly degraded after mechanical stimulus in vitro and in vivo.
(A) FSS causes the rapid loss of sclerostin protein through a number of molecular mediators. (B) Ocy454 cells (n = 3–4) or (C) UMR106 cells (n = 3) were exposed to 1 min of FSS at 4 dynes/cm2 and lysed 5 min post-flow. Western blots were probed for sclerostin, GAPDH, pCaMKII, and total CaMKII. (D) Sixteen week old female C57Bl/6 mice were ulnar loaded (1800 με, 90 s, 2 Hz), cortical osteocyte-enriched lysates isolated 5 min post-load, and western blots probed for sclerostin (n = 10 mice), pCaMKII, and total CaMKII (n = 5 mice). Sclerostin abundance relative to the loading control or pCaMKII relative to total CaMKII was quantified. (E) Ocy454 cells with endogenous sclerostin (n = 2), (F) UMR106 cells with endogenous sclerostin (n = 4), or (G) Ocy454 cells transfected with Myc-tagged sclerostin (n = 1) were subjected to 5 min of FSS at 4 dynes/cm2 and lysed at the indicated times post-flow. Western blots were probed for sclerostin and β-actin. A representative time course is shown for each. Sclerostin abundance relative to the loading control was quantified. For each antibody, western blots are from a single gel and exposure; a vertical black line indicates removal of irrelevant lanes. Graphs depict mean ± SD. *p<0.05, **p<0.01 by unpaired two-tailed t-tests (B–D).