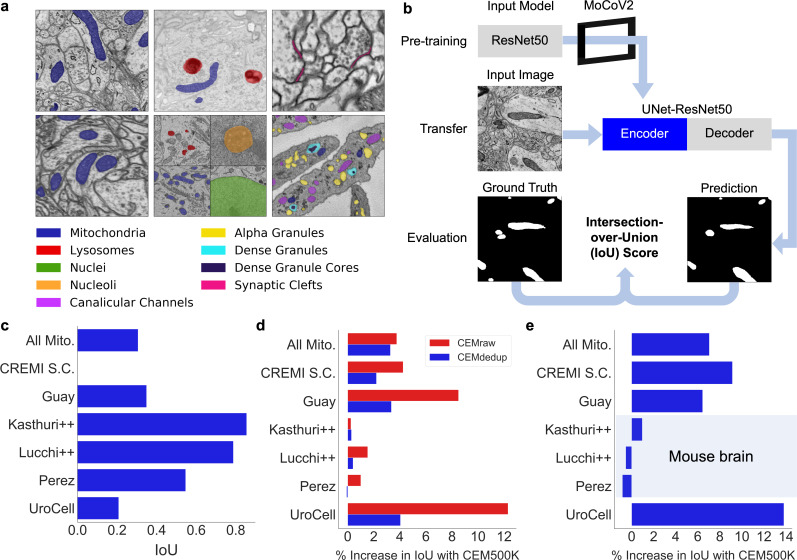
Figure 2. CEM500K pre-training improves the transferability of learned features.
(a) Example images and colored label maps from each of the six publicly available benchmark datasets: clockwise from top left: Kasthuri++, UroCell, CREMI Synaptic Clefts, Guay, Perez, and Lucchi++. The All Mitochondria benchmark is a superset of these benchmarks and is not depicted. (b) Schematic of our pre-training, transfer, and evaluation workflow. Gray blocks denote trainable models with randomly initialized parameters; blue block denotes a model with frozen pre-trained parameters. (c) Baseline Intersection-over-Union (IoU) scores for each benchmark achieved by skipping MoCoV2 pre-training. Randomly initialized parameters in ResNet50 layers were transferred directly to UNet-ResNet50 and frozen during training. (d) Measured percent difference in IoU scores between models pre-trained on CEMraw vs. CEM500K (red) and on CEMdedup vs. CEM500K (blue). (e) Measured percent difference in IoU scores between a model pre-trained on CEM500K over the mouse brain (Bloss) pre-training dataset. Benchmark datasets comprised exclusively of electron microscopy (EM) images of mouse brain tissue are highlighted.