FIG. 2.
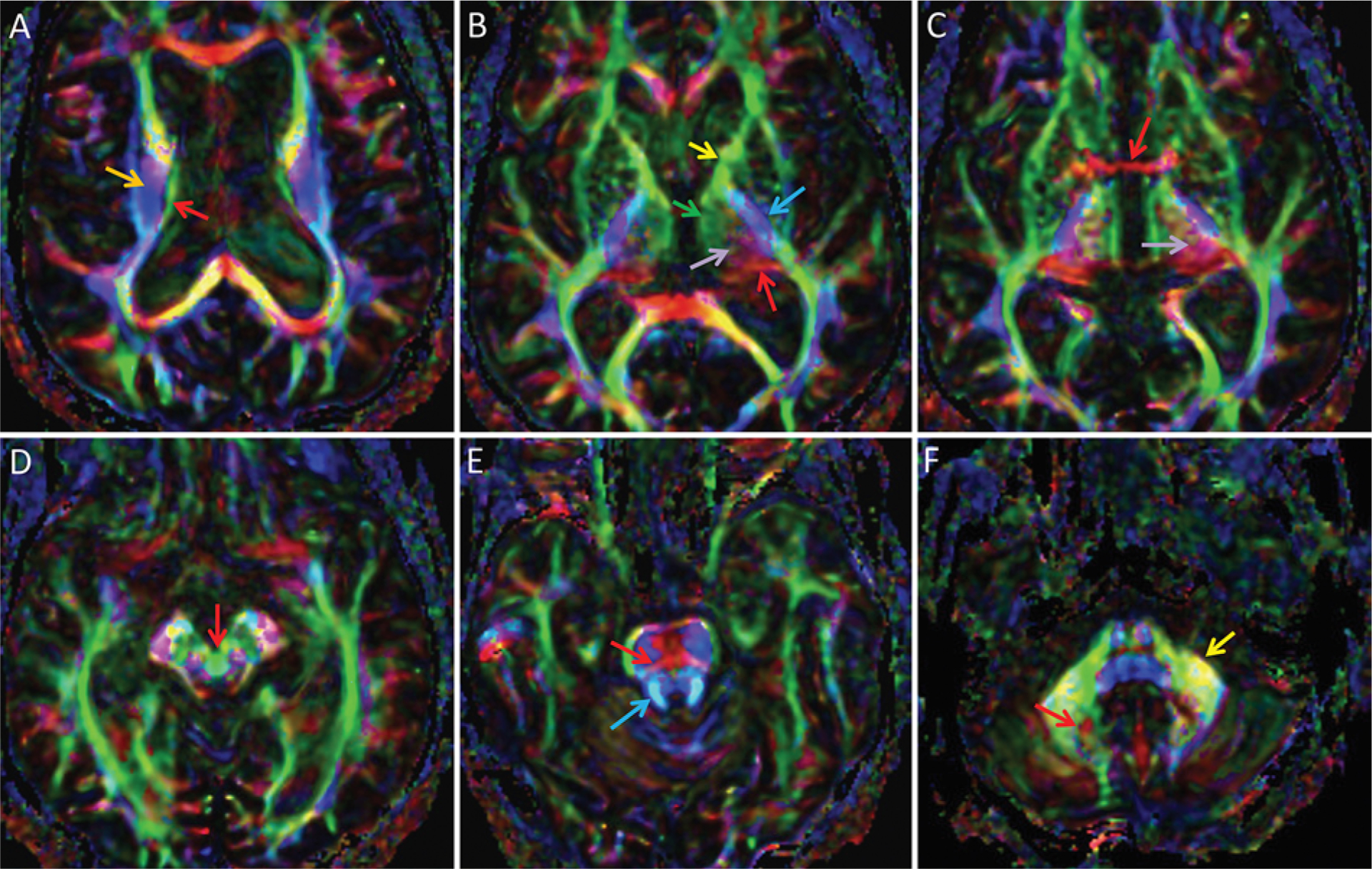
DTI color FA maps of the thalamus and bordering structures, superior to inferior. By standard convention, white matter tracts are color-coded by orientation of their courses: anterior-to-posterior is green, left-to-right is red, and superior-to-inferior is blue; oblique fibers are a blend of these colors. In general, some general regions within the thalamus can be discerned and some important adjacent white matter tracts are identifiable, but individual thalamic nuclei and related white matter tracts are not individually distinguishable. A: Superiorly, the stria terminalis is seen as a green line (red arrow) demarcating the superior thalamus, medial to the corona radiata (orange arrow). B: The medial thalamus is represented in green (green arrow) and is continuous with the anterior limb of the internal capsule (yellow arrow), while the posterior thalamus at the expected location of the pulvinar is red (red arrow). Superolaterally projected tracts between the medial (green) and posterior (red) thalamus are depicted in purple (light purple arrow). This purple region should contain both the DRT and somatosensory fibers associated with VIM and Vc, but these 2 tracts cannot be differentiated. The posterior limb of the internal capsule (blue arrow) contains the pyramidal tract and demarcates the lateral thalamus. C: The inferior thalamus at the level of the AC (red arrow) again demonstrates complex color, but overall there is a green region medially, a red region posteriorly, and a juxtaposed purple region (light purple arrow). D: The decussation of the superior cerebellar peduncles is seen as a circle within the midbrain (red arrow). There, the circle is green, although the color is more typically red, representing predominantly left-to-right crossing fibers including the DRT. E: The superior cerebellar peduncles, which contain the cerebellar efferent fibers such as the DRT (blue arrow) and the transverse pontine fibers (red arrow), are visualized in an image of the superior pons. F: The efferent cerebellar fibers can be followed inferiorly to the region along the medial dentate, which is visualized as an area of complex color (red arrow) near the middle cerebellar peduncle (yellow arrow).
