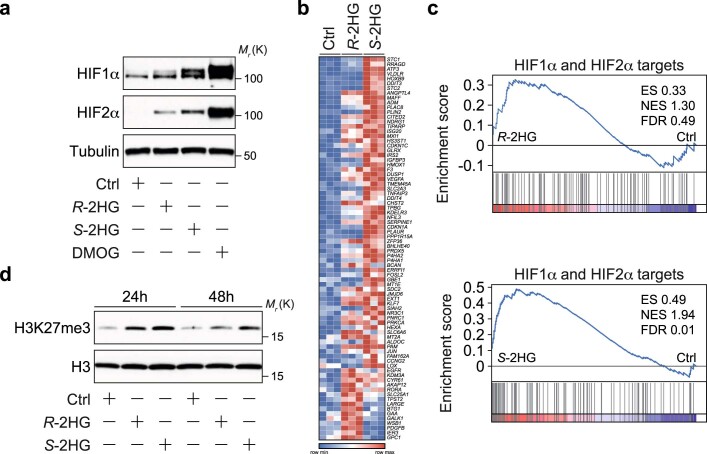
Extended Data Fig. 2. R- and S-2HG reduce the activity of 2-oxoglutarate-dependent dioxygenases in ECs.
a, Immunoblot analysis of HIF1α and HIF2α protein abundance in HUVECs stimulated with cell-permeable R- or S-2HG for 24h. HUVECs treated with vehicle (DMSO) were used as a control (Ctrl). The PHD inhibitor DMOG, which stabilizes HIF protein levels, was used as a positive control. b, Heatmap of hypoxia associated genes that are differentially regulated in control (Ctrl) versus R-2HG or S-2HG-treated HUVECs. DMSO was used as a vehicle control. Cells were stimulated for 24h before total mRNA was collected for RNA-seq analysis, (n=3 independent samples). c, Gene set enrichment analysis (GSEA) showing a HIF gene expression signature in HUVECs treated with R- and S-2HG for 24h when compared to Ctrl. ES, enrichment score; NES, normalized enrichment score; FDR, false discovery rate. d, Immunoblot analysis showing increased histone H3 lysine 27 tri-methylation (K27me3) levels in HUVECs treated with R-2HG or S-2HG when compared to Ctrl. Cells were analysed 24 or 48h after stimulation. Total levels of histone H3 are shown as protein loading control. Western blot data in a and d were from the respective experiment, processed in parallel, and are representative of at least three independent experiments. Unprocessed western blots are provided as source data.