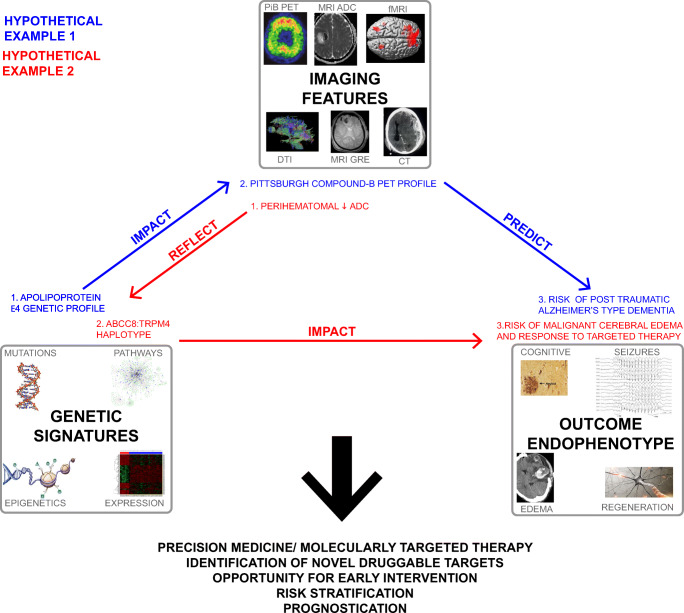
Fig. 5.
Future vision of radiogenomics in moderate/severe TBI. This schematic demonstrates relationships between genetic signatures, imaging characteristics, and endophenotype outcomes after msTBI. Genetic signatures can be in the form of mutations, regulation, expression profiles, and epigenetics for single-genes or pathways. Different genetic signatures impact specific outcome phenotypes (for example: neurodegeneration/cognition, seizures, cerebral edema, neural regeneration). Some of these outcome endophenotypes may be detected acutely (e.g. cerebral edema), whereas others may have a temporal lag varying from days-years until clinical detection (seizures, neurodegeneration). Imaging features may serve as surrogates for certain outcome endophenotypes- for example, MRI based ADC hypointensity may reflect cytotoxic edema, or PiB detection of amyloid aggregation may portend risk for Alzheimer’s Disease. Genetic signatures can thus be linked to imaging features as proxies for an endophenotypic outcome, or interpreted synergistically. Hypothetical example 1 (blue) suggests that a specific APOE e4 genotype (blue-1, genetic signature) results in a certain PiB-PET profile (blue-2, imaging feature); these two features combined may predict risk of post-traumatic Alzheimer’s type dementia (blue-3, endophenotype outcome). Hypothetical example 2 (red) indicates that detection of perihematomal ADC reduction (red-1, imaging feature) reflects a specific ABCC8:TRPM4 haplotype (red-2, genetic signature); this haplotype impacts risk of malignant cerebral edema and mediates response to therapy. (Of note, ABCC8 and TRPM4 encode subunits of an octameric cation channel known to mediate cerebral edema after brain injury). Identifying the relationship between genetic signatures, imaging features, and outcome endophenotypes for different secondary injury processes will facilitate precision medicine, identification of novel targets, opportunities for early intervention, risk stratification and prognostication, ABCC8 = ATP binding cassette subfamily C member-8; ADC = apparent diffusion coefficient; APOE-e4 = apolipoprotein E epsilon 4; MRI = magnetic resonance imaging; msTBI = moderate-severe TBI; PET = positron emission tomography, PiB = Pittsburgh compound B, TRPM4 = transient receptor potential cation channel subfamily M.