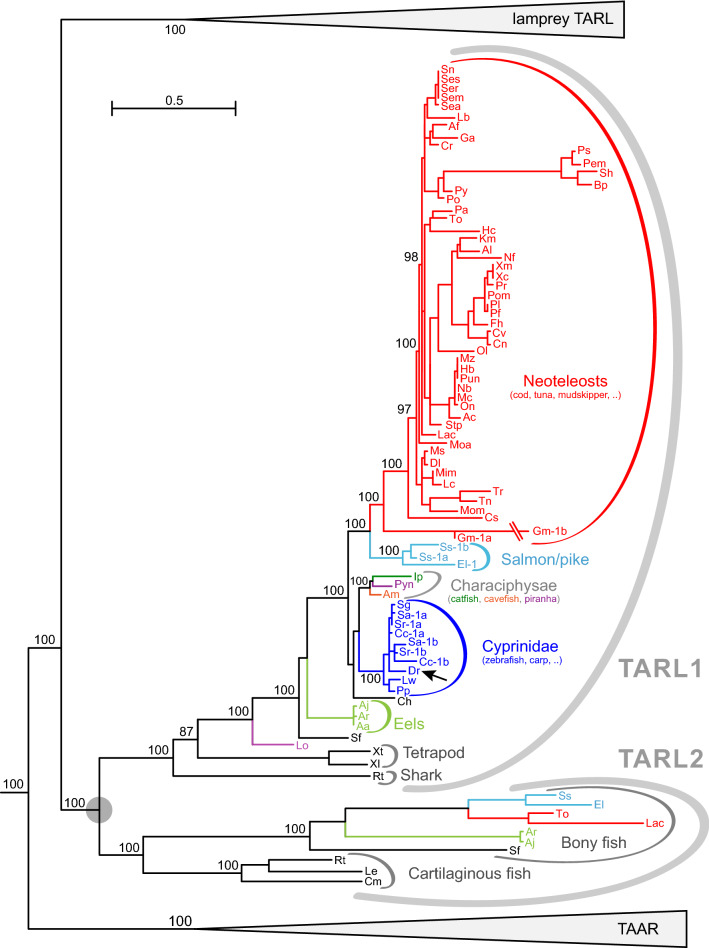
Figure 3.
Phylogenetic tree of cartilaginous and bony fish taar-like genes. Phylogenetic tree of taar and taar-like genes, with all nodes collapsed (grey triangles) except bony and cartilaginous fish taar-like genes (ancestral node denoted by grey circle). Gene set and tree construction are same as in Fig. 1. Species are indicated by the initials of their Latin names, see Table 1 for full names, gene names as indicated. Note a basal duplication of the ancestral tarl gene into tarl1 and tarl2 clades. Late gene duplications are denoted by letters, e.g. Cc-1b stands for tarl1b of crucian carp. Note that this gene tree closely follows the corresponding species tree, with cartilaginous fish TARL occupying basal nodes, and TARL from earlier-derived bony fish (spotted gar, eel) basal in the bony fish TARL clade. Black arrow, zebrafish TARL1, whose expression is shown in Fig. 4. Without exception, neoteleost TARL are situated in the most-derived sub-clade (red). Numbers indicate % branch support for basal nodes (cutoff 80%). Scale bar, number of amino acid substitutions per site.