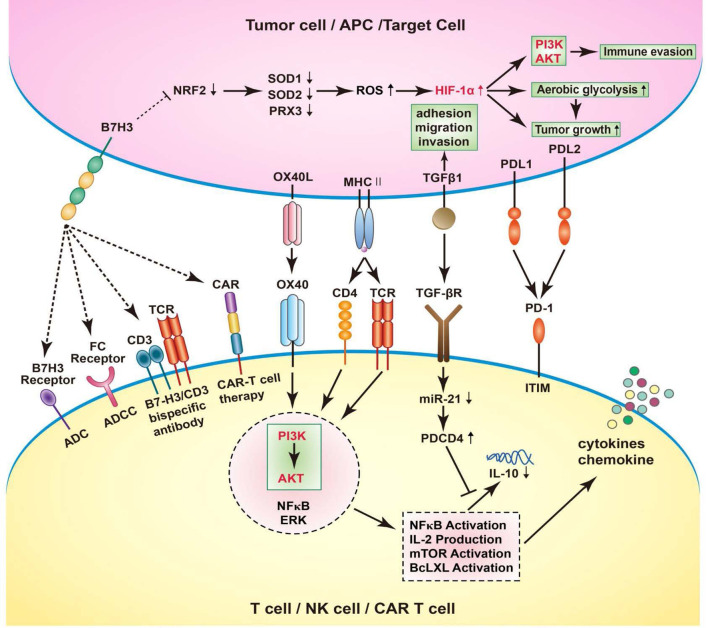
Figure 2.
B7-H3 increases ROS and HIF-1α through B7-H3-induced Nrf2 suppression, SOD1, SOD2, and PRX3 reduction, thus promote aerobic glycolysis in cancer cells, leading to tumor growth. Human cancer immunotherapy strategies targeting B7-H3 including blockade of B7-H3 with blocking monoclonal antibodies (mAbs); B7-H3 specific antibody-dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC); CD3/B7-H3 bispecific antibodies; Small molecule inhibitors; Engineered chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T cells; combination with other therapies. In T cells, OX40 engagement by OX40L forms a signaling complex with a number of established pro-inflammatory mediators, including AKT, PI3K, NFkB, ERK. Through the PI3K/AKT signaling pathway, the downstream signatures were activated, such as NFkB activation, IL-2 production, mTOR activation, BcLXL activation. As a result, NFkB activation stimulates the expression of chemokines and cytokines, including IL-10. Interestingly, the activation of TGFB1 receptor could simultaneously suppress the maturation of miR-21 and enhance PDCD4 levels. Consequently, the translation of the anti-inflammatory cytokine IL-10 is inhibited. In RCC cells, the TGFBI could participate in the adhesion, migration, and invasion, depending on the inactivation of VHL.