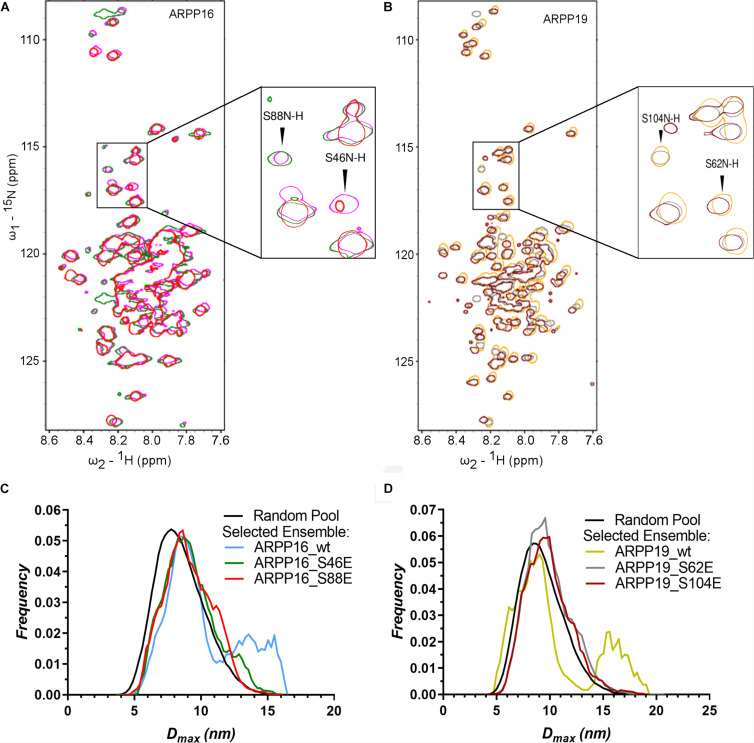
FIGURE 5.
The phosphorylation does not have significant effect on the structural properties of ARPPs. (A,B) The overlay 2D 15N-HSQC spectra of uniformly 15N labeled ARPP WT and phosphomutants reveals that the phosphomimicking mutations have no significant effect on ARPPs’ structural properties. The cross peaks in the 15N-HSQC spectra of both ARPP-16 and ARPP-19 phosphomutants are highly similar to WT spectra, showing low dispersion of amide proton chemical shifts. This indicates that the ARPPs’ phosphomutants do not induce formation of well-defined 3D structure. (A) The spectrum of WT ARPP-16 is shown in magenta, ARPP-16 S46E and ARPP-16 S88E in green and red, respectively. (B) The spectrum of WT ARPP-19 is shown in orange, ARPP-19 S62E and ARPP-19 in gray and maroon, respectively. (C,D) Dmax distributions of ARPPs’ WT and phosphomutants ARPPs obtained from EOM analyses of the SAXS data plotted as function of frequency (a.u.) reveals that with phosphomutants, the extended conformation is less favored than with WT.