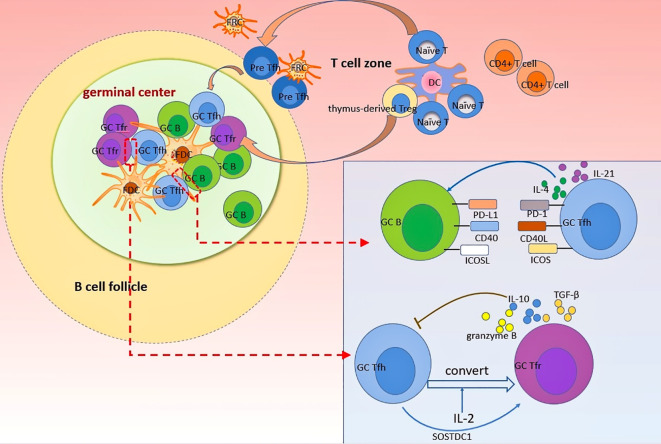
Figure 1.
Dynamics of Tfh and Tfr cells in GC response. Naïve T cells and thymus-derived Treg can differentiate into Tfr and Tfh cells, respectively, after the priming by dendritic cells. Differentiated Tfr and Tfh cells gradually migrate into follicles in a CXCR5-dependant manner to exert profound impacts on GC B cells. Follicular stromal cells such as FDC provide an important plat form for various cellular interaction. In GC, Tfh cells support B cells differentiation and antibodies production by providing essential signals to B cells through direct interactions mediated by PD-1, CD40L, and ICOS, as wells as cytokines such as IL-4 and IL-21. By contrast, Tfr cells uniquely inhibit the differentiation and function of Tfh cells through secreting several anti-inflammatory cytokines (including IL-10, TGF-β, granzyme B) to suppress the GC response. The crosstalk between Tfr and Tfh cells is complex. Tfh cells can convert into Tfr cells after stimulation by IL-2. Moreover, SOSTDC1-producing Tfh cells can serve as an inducer of Tfr cells.