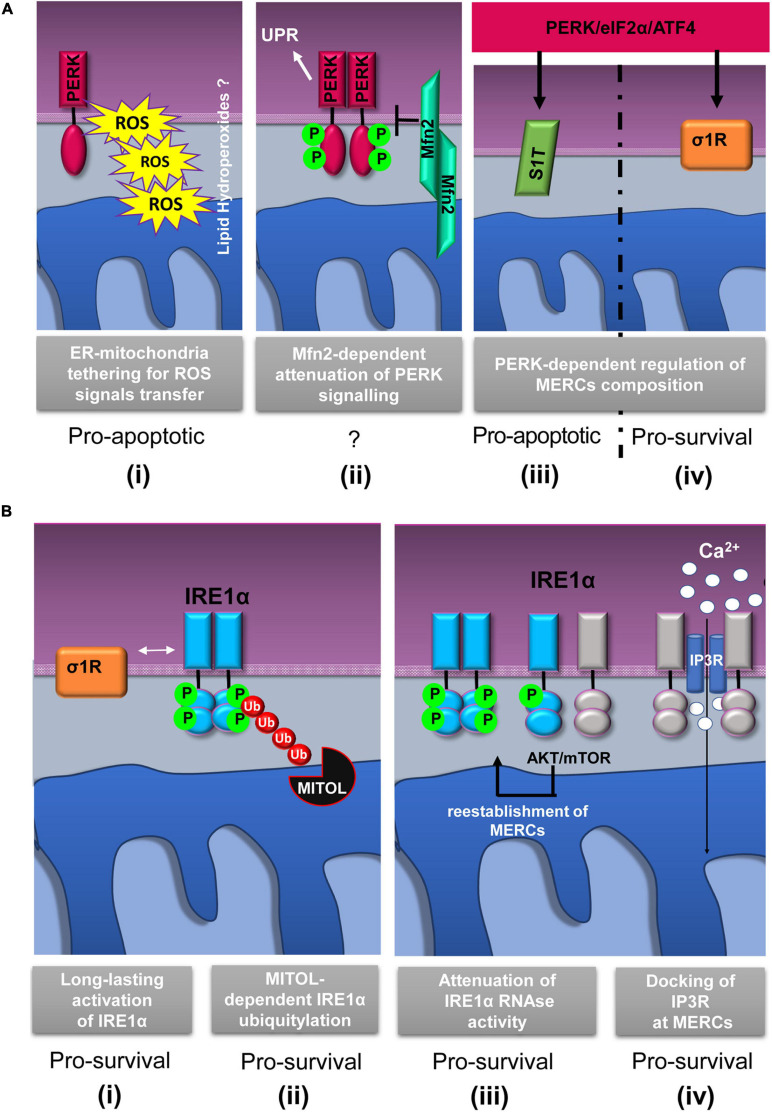
FIGURE 2.
Schematic representation of relevant events involving IRE1α and PERK proteins at mitochondria–ER contacts (MERCs). (A) PERK-involving events at MERCs: (i) PERK tethers the ER to mitochondria promoting the rapid transfer of reactive oxygen species (ROS) signals, likely under the form of lipid hydroperoxides (Verfaillie et al., 2012); (ii) Mitofusin 2 (Mfn2) lies upstream of PERK and under basal conditions maintains PERK inactive (Munoz et al., 2013); the PERK/eIF2α/ATF4 signaling pathway upregulates the expression of SERCA1 truncated proteins (S1T) (iii) and sigma-1 receptor (σ1R) (iv) at MERCs (Chami et al., 2008; Mitsuda et al., 2011). (B) Events involving IRE1α at MERCs: (i) σ1R-dependent stabilization of IRE1α oligomerization at MERCs (Mori et al., 2013); (ii) mitochondrial ubiquitin ligase (MITOL)-dependent ubiquitylation of IRE1α at MERCs prevents ER stress induced apoptosis (Takeda et al., 2019); (iii) the AKT-mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR) signaling attenuates IRE1 RNase activity by promoting the re-establishment of ER-mitochondria contacts (Sanchez-Alvarez et al., 2017); (iv) IRE1α scaffolds IP3R at MERCs to sustain calcium transfer and mitochondrial bioenergetics (Carreras-Sureda et al., 2019). The putative pro-survival or pro-apoptotic outputs of the depicted events are reported.