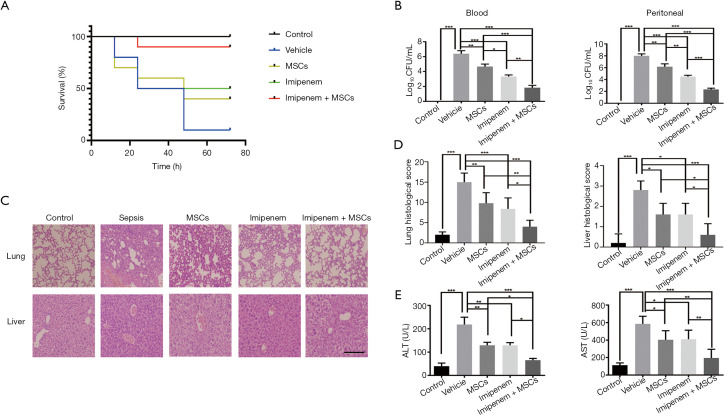
Figure 1.
UC-MSCs improve the survival rate of imipenem monotherapy and ameliorate organ injury in E. coli-induced septic mice. Septic mice were treated with UC-MSCs and imipenem together or separately 4 h after E. coli infection (1×108 CFU/mouse). Mice in the control group were treated with PBS. The survival rate of each group was monitored every 12 h for 3 days. (A) Kaplan-Meier curves were used to analyze survival rates (n=10). (B) In a separate experiment, mice were treated as in (A) except they were anesthetized and killed 24 h after E. coli infection. Blood and peritoneal fluid were collected and plated for 16 h. Statistical analysis of the CFU number is shown (n=5). (C) Lung and liver tissues were analyzed using HE staining (original magnification, ×20); the scale bar represents 150 µm. (D) Injury scores of lungs and livers in different experimental groups (n=5). (E) Serum concentration of ALT and AST were measured (n=5). The data are presented as the mean ± SEM. The experimental data shown in this figure are representative of three independent experiments. *, P<0.05; **, P<0.01; ***, P<0.001. UC-MSC, umbilical cord mesenchymal stem cell; E. coli, Escherichia coli; PBS, phosphate-buffered saline; HE, hematoxylin and eosin; ALT, alanine aminotransferase; AST, aspartate aminotransferase.