Figure 7. Drug combinations induce toxicity in patient‐derived organoids and sensitize to paclitaxel treatment.
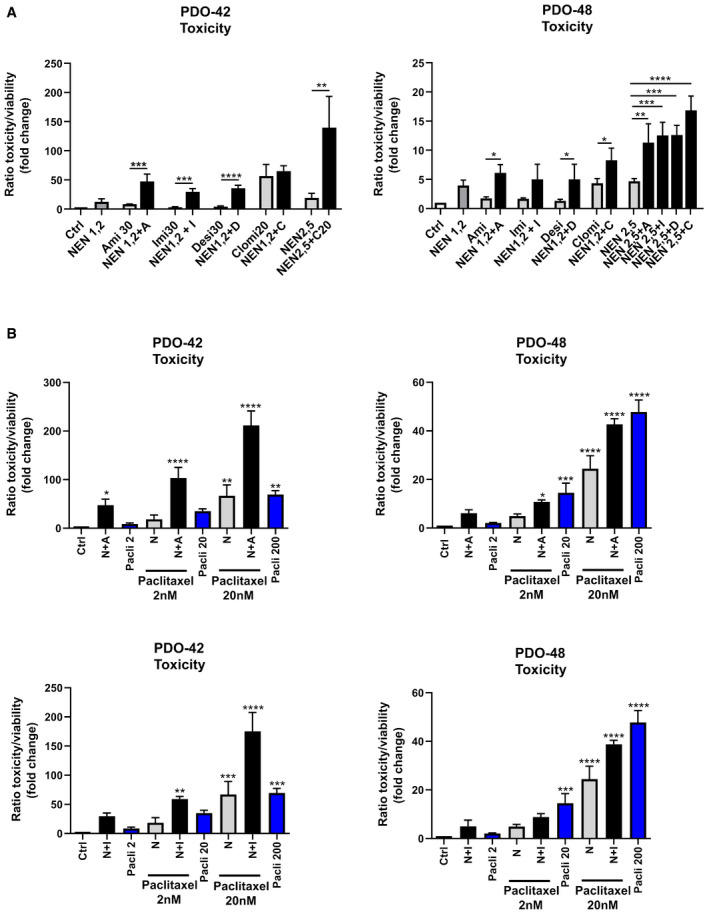
- Ratio of toxicity and viability determined in pancreatic cancer‐derived organoids from two patients ((left) PDO‐42 and (right) PDO‐48) treated as indicated for 3 (PDO‐42) or 5 (PDO‐48) days. Significant differences are shown for the comparison between single and combined drug treatments as indicated (NEN 1.2 µM or 2.5 µM, amitriptyline (Ami, A), imipramine (Imi, I), desipramine (Desi, D), each 30 µM, clomipramine (Clomi, C) 20 µM).
- Ratio of toxicity and viability determined in pancreatic cancer‐derived organoids from two patients ((left) PDO‐42 and (right) PDO‐48) treated as indicated for 3 (PDO‐42) or 5 (PDO‐48) days. Significant differences are shown for the comparison between drug treatments as indicated to the control condition (NEN (N) 1.2 or 2.5 µM, amitriptyline (A), imipramine (I) 20 µM, paclitaxel (Pacli), 2, 20 or 200 nM). As references for sensitization effects to standard chemotherapy, the bars showing single paclitaxel treatments using the indicated concentrations are highlighted in blue. Bars for controls (Ctrl), paclitaxel (Pacli), NEN (N) alone, and combined NEN + paclitaxel treatment are identical in the individual graphs (including respective graphs in Fig EV5A) for comparison to combinations with the respective TCA drugs as indicated.
Data information: In (A and B), data are presented as mean (SD) (N = 3) and were analyzed by a one‐way ANOVA with Tukey post hoc test. *P < 0.05; **P < 0.01; ***P < 0.001; ****P < 0.0001. Exact P‐values for all comparisons are listed in Appendix Table S1.
