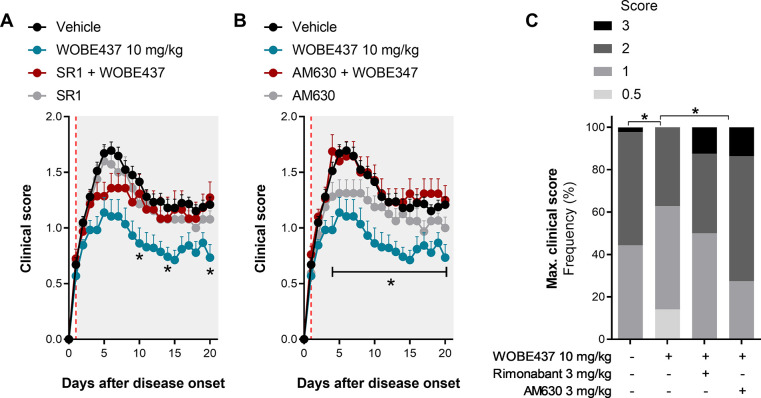
Figure 2.
Evaluation of either CB1 or CB2 receptor antagonism in combination with WOBE437 treatment in EAE female C57BL/6 mice. (A, B) Time course of clinical score from day 0 to day 20 in mice administered with either a (A) CB1 antagonist or (B) CB2 antagonist, in combination with WOBE437 (10 mg/kg) or vehicle (DMSO); onset is represented at day 1 (red line). (C) Maximal clinical score observed during the time course of clinical score, from day 0 to day 20. Rimonabant (SR1, 3 mg/kg) was used as CB1 receptor antagonist/inverse agonist, and AM630 (3 mg/kg) was used as CB2 receptor antagonist/inverse agonist. Administration of vehicle and all compounds started at the individual day of onset (day 1) of each mouse; injections (20 μL) were done i.p. once per day during 20 days. Data show (A, B) mean ± SEM or (C) cumulative frequency; group sizes (mice per group) were as follows: vehicle n = 37, WOBE437, n = 29; SR1, n = 17; SR1 + WOBE437, n = 20; AM630, n = 16; AM630 + WOBE437, n = 21. Data show the summary of two or four different cohorts; only mice showing symptoms were included in the study. Statistical differences were determined using (A, B) multiple t-test corrected for multiple comparison with the Holm–Sidak method or (C) chi-square test and Fisher’s exact test. *, p < 0.05 comparing as indicated by brackets or comparing WOBE437 against SR1 + WOBE437 or against AM630 + WOBE437.