Figure 1.
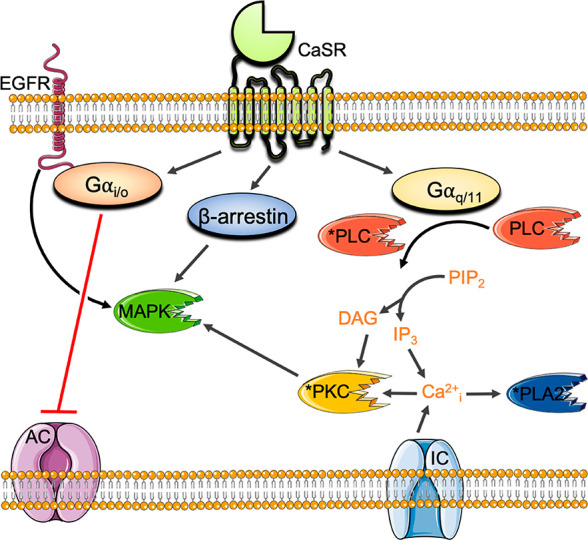
Principal CaSR signaling pathways. CaSR activation of Gi/o inhibits adenylyl cyclase (AC) to reduce cAMP levels. CaSR coupling to Gq/11 activates phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C (PI–PLC) to increase inositol triphosphate (IP3) and diacyl glycerol (DAG) and trigger the release of Ca2+i from stores. Ca2+i activates phospholipase A2 (PLA2) and PKC. The CaSR also increases Ca2+i via influx through L-type voltage-gated and transient receptor potential ion channels (IC), in part via PKC. The CaSR activates MAPK signaling cascades via Gq/11-mediated PKC, Gi/o-mediated activation of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), and β arrestin.
