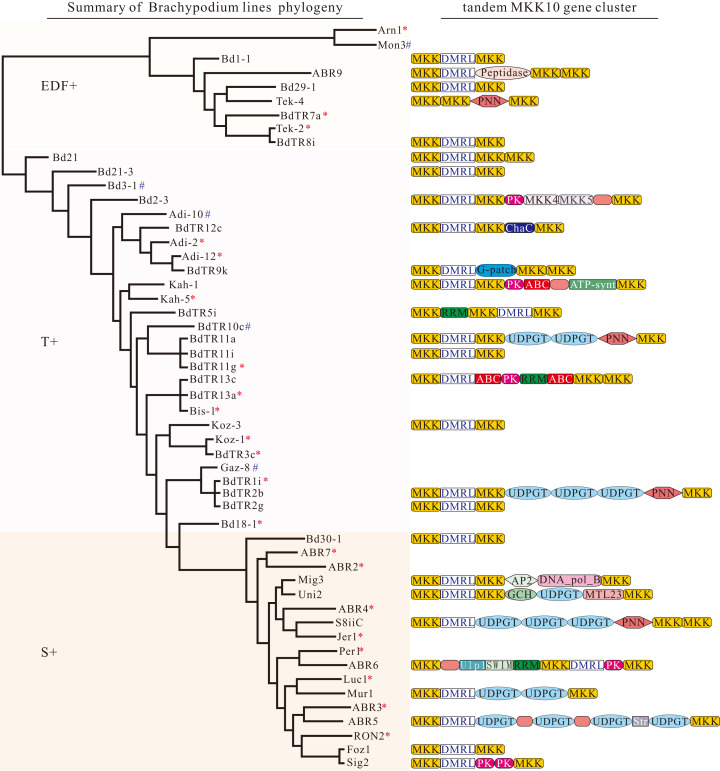
Figure 6. The diversity and evolution of the fate of an ancestral locus having B. distachyon inbred lines MKK10 genes in tandem position.
Phylogenetic relationships among 53 diverse B. distachyon inbred lines were investigated. The phylogenetic tree is modified from BrachyPan (https://brachypan.jgi.doe.gov/). The variants of ancestral tandem MKK10 gene clusters in B. distachyon inbred lines are shown on the right. The red asterisk indicates the gene cluster models of these inbred lines are same as Bd21, while blue pound represents no tandem duplication events. Gene or protein names: MKK (MAPK kinase 10); DMRL ( DMRL synthase ); Peptidase (Peptidase_C48); PNN (pinin); ChaC (ChaC-like protein); G-patch (glycine rich nucleic binding domain); ATP-synt (ATP synthase subunit C); RRM (RNA recognition motif protein); UDPGT (UDP-glucoronosyl and UDP-glucosyl transferase); ABC (ABC transporter); PK (Protein tyrosine kinase); AP2 (AP2/EREBP transcription factor); DNA_pol_B (DNA polymerase family B); GCH (Predicted glycine cleavage system H protein); MTL23 (Methyltransferase-like protein 23); Ulp1 (Ulp1 protease); SWIM (SWIM zinc finger); Str (Strictosidine synthase).