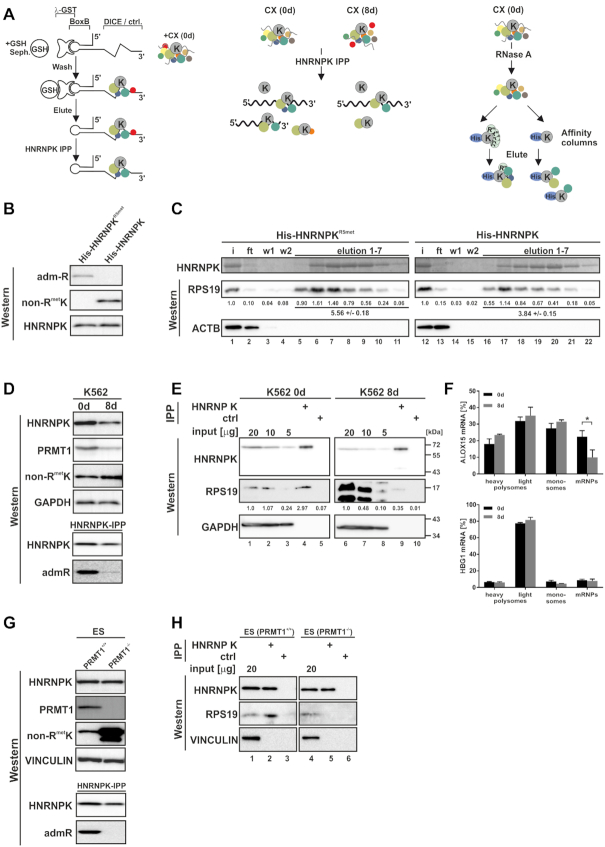
Figure 2.
HNRNPK arginine methylation affects RPS19 binding. (A) Purification strategies that identified HNRNPK interacting proteins of the translational silencing complex listed in Table 1. Left panel: DICE-BoxB-RNA linked to GSH-sepharose via GST-tagged λ peptide (45) was incubated with translation competent cytoplasmic extract (CX) of noninduced K562 cells (0 d) and eluted DICE-RNA-bound complexes were further purified by HNRNPK immunoprecipitation (IPP) (28). Middle panel: K562 CX (0 d) and CX of cells induced 8 days for erythroid maturation (8 d) were subjected to HNRNPK IPP to enrich proteins differentially associated with HNRNPK (16). Right panel: RNase A-treated K562 CX (0 d) was utilized for affinity purification employing either recombinant quantitatively asymmetrically dimethylated His-HNRNPKR5met (17,32) or nonmethylated His-HNRNPK, which represent the methylation state of endogenous HNRNPK at day 0 and 8 of erythroid maturation, respectively (16). (B) Specific detection of His-HNRNPKR5met and His-HNRNPK by monoclonal antibodies generated against asymmetrically dimethylated arginine residues (admR) (46) or nonmethylated HNRNPK (non-RmetK) (16), respectively. (C) Recombinant His-tagged methylated HNRNPKR5met (lanes 1–11) or nonmethylated HNRNPK (lanes 12–22) were immobilized on Ni-NTA agarose and incubated with RNase A treated CX of K562 cells (0 d). HNRNPK was eluted with imidazole and visualized by Coomassie staining, interacting RPS19 with a specific antibody. Co-eluted RPS19 was quantified below (n = 3). ACTB served as control. (D) Upper panel: HNRNPK and PRMT1 expression in K562 cells at 0 d and 8 d and non-RmetK level. GAPDH served as control. Lower panel: HNRNPK IPP indicating predominant HNRNPK methylation at 0 d detected with the admR antibody. (E) HNRNPK IPP (lanes 4, 9) and control IPP (lanes 5, 10) from K562 0 d CX (input, lanes 1–3) and 8 d CX (input, lanes 6–8). HNRNPK and RPS19 were analyzed by western blotting, levels of RPS19 shown beneath. Representative blots were quantified from three independent experiments. (F) Ribosomal association of ALOX15 (CDS 1986 nts) mRNA and HGB1 (CDS 444 nts) mRNA fractionated upon sucrose gradient centrifugation in three independent experiments (means ± s.d.; n = 3). (G) Upper panel: Levels of HNRNPK, PRMT1, non-RmetK and Vinculin in extracts of ES (PRMT1+/+) and (PRMT1−/−) cells. Lower panel: HNRNPK IPP verifying lack of HNRNPK methylation in ES (PRMT1−/−) with admR antibody. (H) HNRNPK IPP (lanes 2, 5) and control IPP (lanes 3,6) from ES (PRMT1+/+) (input, lane 1) and (PRMT1−/−) cell extracts (input, lane 4). HNRNPK and RPS19 were detected by Western blotting.