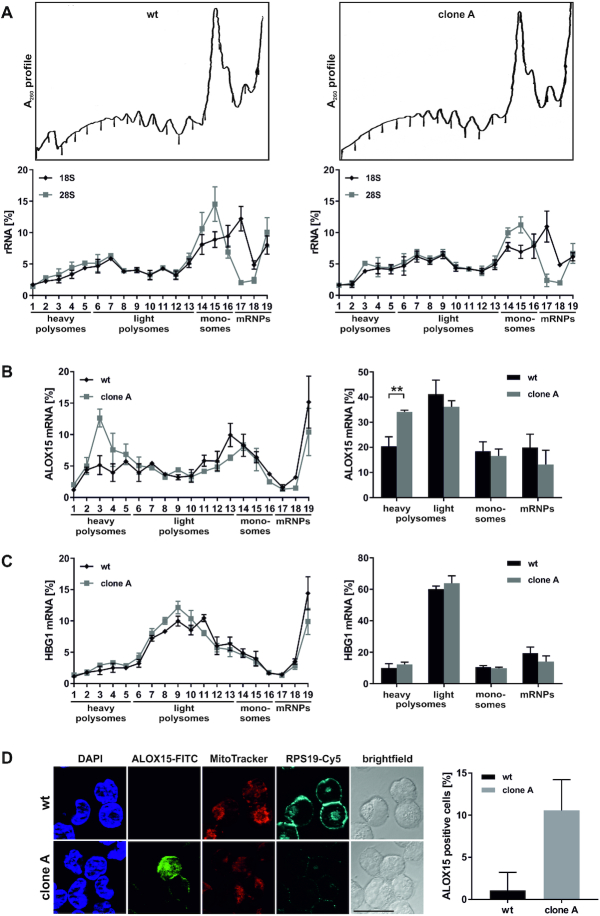
Figure 7.
RPS19 depletion results in derepression of ALOX15 mRNA translation. (A–C) K562 wt cells (left) or RPS19 shRNA clone A cells (right) were treated with cycloheximide, lysed and fractionated on 15–45% sucrose gradients. (A) Upper panels: representative λ = A260nm fractionation profiles. Lower panels: 18S and 28S rRNA distribution in gradient fractions analyzed by RT-qPCR, normalized to blaR extraction control and input RNA (n = 3, mean ± SEM). (B) Left panel: distribution of ALOX15 mRNA determined as in (A). Right panel: ALOX15 mRNA in heavy and light polysomes, monosomes and mRNP (including 40S) fractions, as indicated in the left panel (n = 3, mean ± SD, two-way ANOVA, **P < 0.01). (C) HBG1 mRNA assigned to fractions as in (B). (D) Left panel: Immunofluorescence analysis of noninduced K562 wt cells and RPS19 shRNA clone A with RPS19 and ALOX15 specific antibodies. Nuclei detected with DAPI, functional mitochondria with MitoTracker Orange; scale bar: 20 μm. Right panel: average number of ALOX15 positive cells.