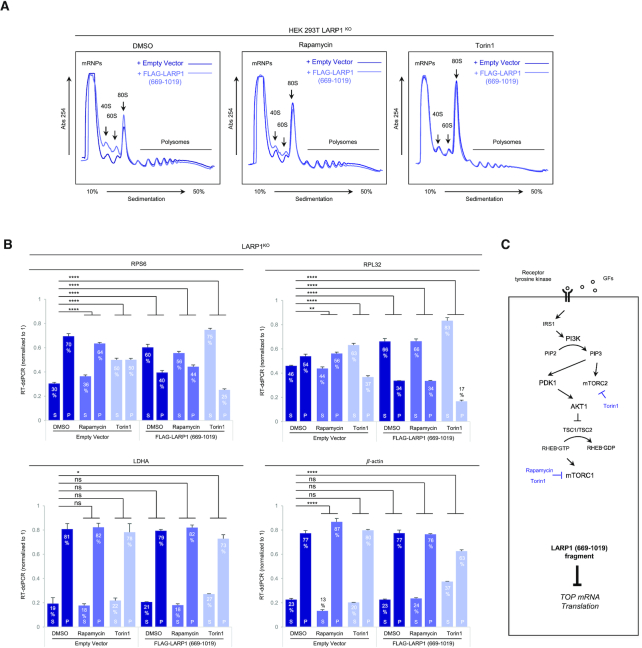
Figure 2.
Overexpression of a C-terminal fragment of LARP1 (spanning residues 669–1019) constitutively represses TOP mRNA translation in an mTORC1-independent manner. (A) HEK293T cells were cultured to near-confluency (∼70–80%) at which point cells were replenished with fresh complete media (containing 10% (v/v) fetal bovine serum) containing either 0.1% (v/v) DMSO (vehicle), 100 nM rapamycin or 300 nM Torin1 for 3 h. Cells were lysed in hypotonic buffer and samples of lysates were subjected to sucrose gradient ultracentrifugation/polysome profile analysis. Absorbance (254 nm) profiles are shown. (B) Total RNA was extracted from each fraction and pooled into subpolysomal (S) and polysomal (P) fractions. cDNA was synthesized from S and P fractions by reverse-transcription (RT) and specific transcripts quantified by droplet digital PCR (ddPCR). Data shown as percentage abundance on S and P fractions. Error bars denote standard deviation (St. Dev.) for three technical replicates. Translation efficiency was determined as the ratio of P/S. (C) Diagrammatic representation of PI3K/AKT/mTORC1 pathway and ability of the cap-binding fragment of LARP1 to constitutively repress TOP mRNA translation.