Figure 3.
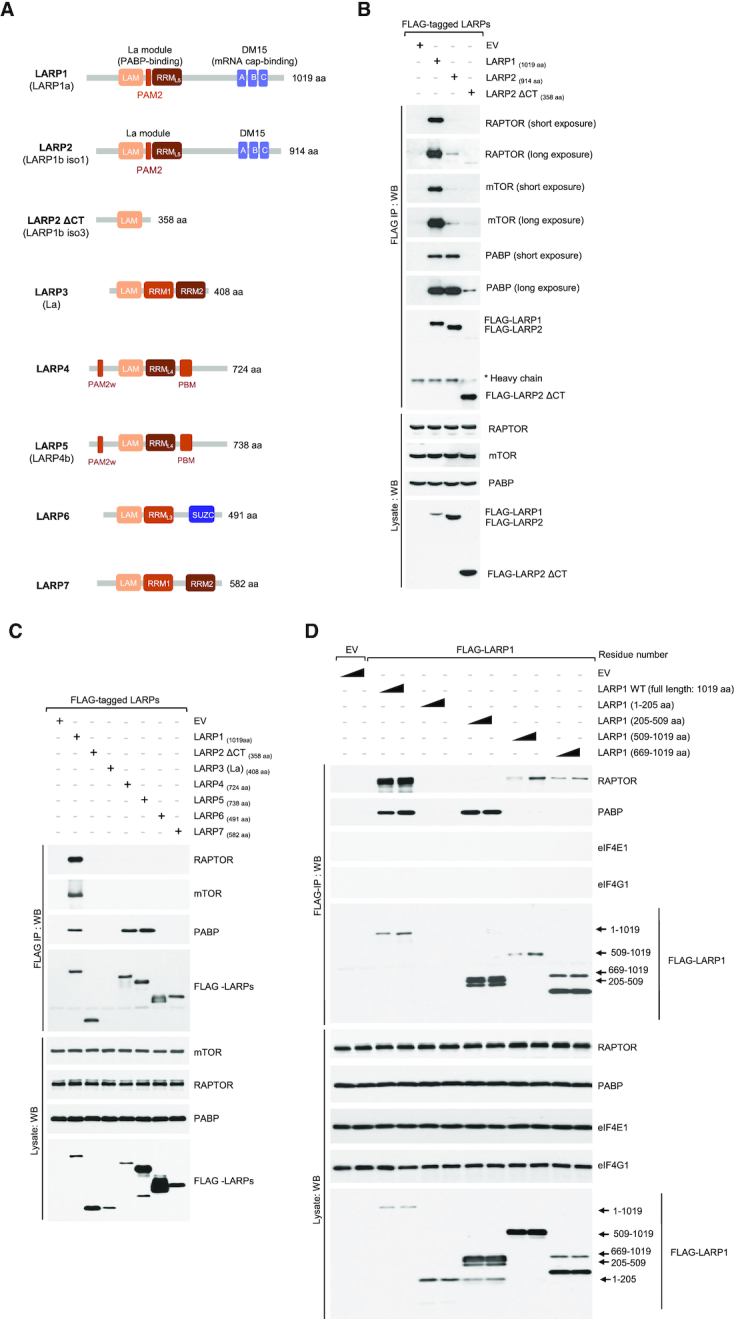
LARP1 and LARP2 bind PABP via the La module, while only LARP1 binds mTORC1 via the DM15 region. (A) Diagrammatic representation of the human LARP superfamily. (B) LARP1 and LARP2 interact with PABP, while only LARP1 binds mTORC1. HEK 293T cells were transiently transfected with empty vector (EV), FLAG-tagged LARP1, –LARP2 or a variant of LARP2 that lacks the C-terminal region (–LARP2 ΔCT). Cells were stimulated with full growth media for 3 h and lysed in CHAPS-based extraction buffer (see Experimental Procedures section). Lysates were subjected to immunoprecipitation (IP) and analyzed by SDS-PAGE/western blot with the indicated antibodies. (C) LARP1, LARP2, LARP4 and LARP5 interact with PABP. HEK 293T cells were transfected and treated as described in (B) and lysates subjected to IP with anti-FLAG antibody. (D) RAPTOR binds to the C-terminal region of LARP1 that comprises the DM15 domain, while PABP binds to the La module that comprises the previously characterized PAM2 motif. LARP1 does not interact with eIF4G1 or eIF4E1. HEK 293T cells were transfected with empty vector (EV), full length FLAG-tagged wildtype LARP1 (WT) or FLAG-tagged fragments of LARP1. Amino acid numbering indicated. Transfected cells were treated and lysed as described in (A). Lysates were subjected to IP with anti-FLAG antibody and analyzed by SDS-PAGE/western blot with the indicated antibodies. Triangle denotes plasmid DNA concentration
