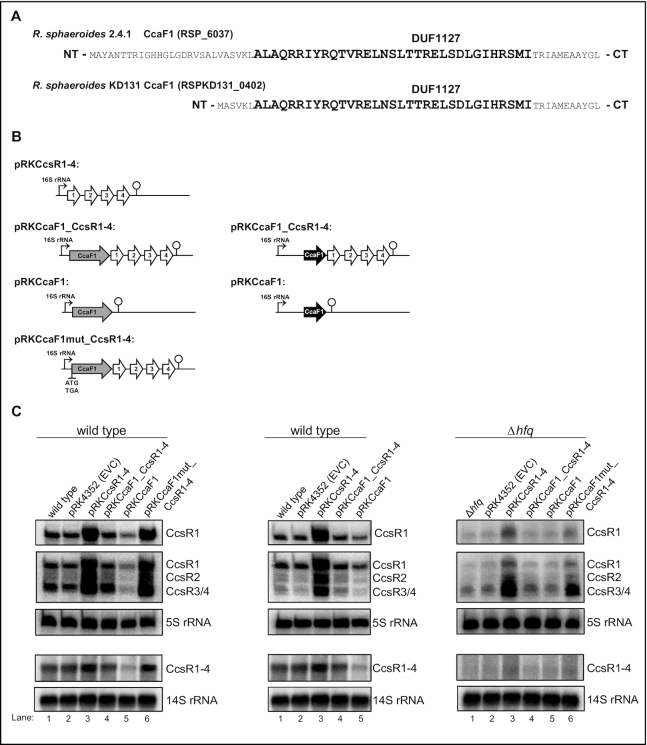
Figure 2.
Small DUF1127 proteins affect CcsR level in R. sphaeroides. (A) Amino acid sequence of the small DUF1127 protein CcaF1 from R. sphaeroides 2.4.1 and the corresponding homologue RSPKD131_0402 from R. sphaeroides KD131. The conserved DUF1127 domain as shown in Supplementary Figure S3 is high-lighted in bold letters. (B) Schematic overview of the plasmids introduced into the wild type strain 2.4.1 or the mutant lacking the hfq gene. The ccaf1 gene is shown in light grey, the RSKD131_0402 gene in black, CcsR RNAs in white. In plasmid pRKCcaF1mut_CcsR1–4 the ATG of the ccaF1 gene was changed to TGA. (C) Northern blots of total RNA from strains containing an empty vector control (pRK4352, EVC) with just the 16S promoter, or plasmids as shown in (B). DNA fragments specific for CcsR1, CcsR2, CcsR3/CcsR4 or CcsR1–4 were used as probes. Signals for 5S RNA or 14S RNA were used as loading controls. R. sphaeroides cleaves the 23S RNA into fragments of 16S and 14S (70). The upper three panels stem from 10% denaturing polyacryamide gels, the lower two panels from 1% formaldehyde agarose gels.