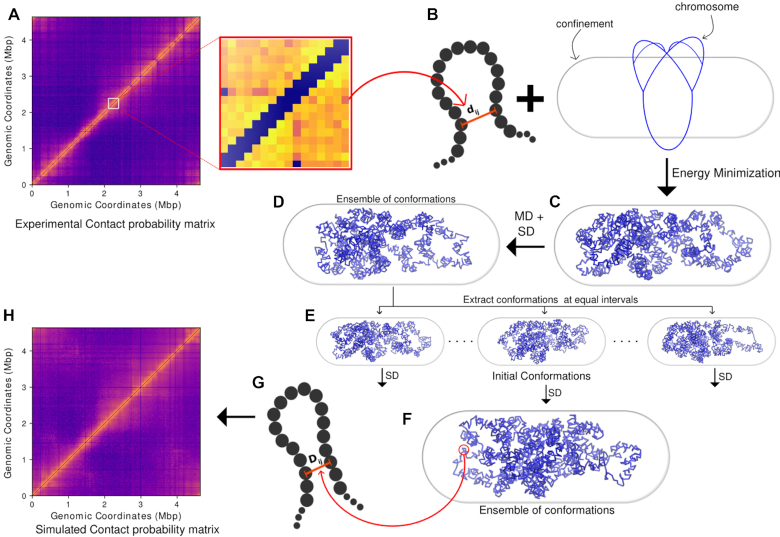
Figure 1.
A schematic of the method used to generate an ensemble of final chromosome structures. (A) Contact probability matrix from Hi–C experiment. (B) Expanded section of the matrix. (C) The experimental contact probabilities are mapped onto bond distances and bond strengths. dij is the initial distance between particles i and j. With Hi–C incorporated as harmonic restraints, the polymer is energy minimized along with the confining potential. (D) The energy minimized conformation is subjected first to molecular dynamics, then stochastic dynamics. (E) From the trajectory obtained via the stochastic dynamics, 200 snapshots were extracted at equal intervals from the last 1000 frames to get 200 initial conformations. (F) The initial conformations are subjected to another stochastic dynamics to obtain an ensemble of conformations. (G) The inter-particle distances obtained from the last 2000 frames of the 200 trajectories (2000 × 200) are used to calculate a simulated Hi–C contact probability matrix. (H) The simulated Hi–C contact probability is filtered and compared with the experimental matrix to validate the model.