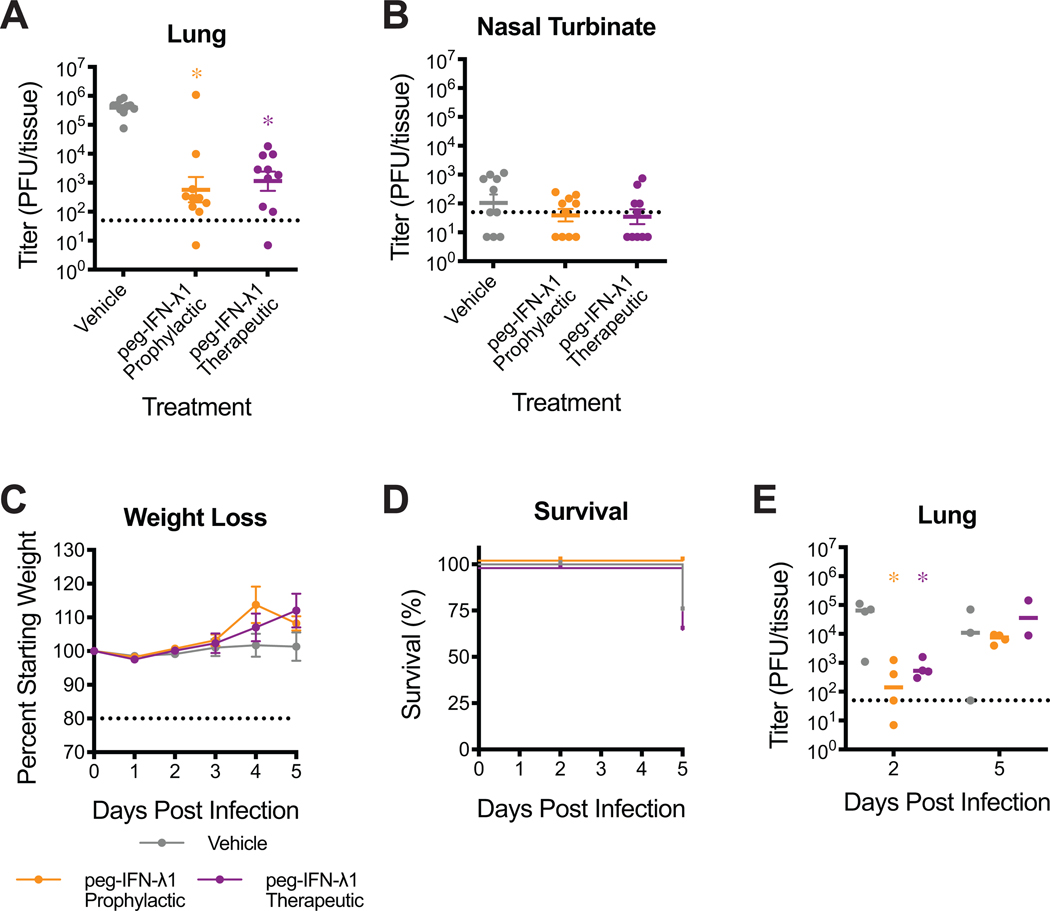
Extended Data 4: Evaluation of peg-IFN-λ1 against SARS-CoV-2 MA infection in young BALB/c and HFH4-hACE2 mice.
(A–B) 12-week-old female BALB/c mice were subcutaneously treated with vehicle or with 2μg peg-IFN-λ1 prophylactically or therapeutically and infected with SARS-CoV-2 MA. Viral titers in the lung (A) and nasal turbinates (B) at 2dpi. n=10 for each group, combined from two independent experiments. Dotted line represents limit of detection (LOD). Undetected samples plotted at half the LOD. Log transformed data analyzed by 1-way ANOVA followed by Holm-Sidak’s multiple comparisons. (A) ‘*’ denotes p=<0.0001 (prophylactic), <0.0001 (therapeutic). (C–E) 4- to 7-week old HFH4-hACE2 male and female mice were treated with peg-IFN-λ1 as done in (A–B) and infected with 105 PFU SARS-CoV-2 WT. n=8 vehicle; n=10 prohpylactic, n=7 therapeutic. (C) Percent starting weight. Dotted line represents weight loss criteria for humane euthanasia. Data analyzed by mixed effects analysis followed by Sidak’s multiple comparisons. (D) Survival. (E) Lung viral titer at 2 and 5dpi. 2dpi: n=4 vehicle, n=4 prophylactic, n=4 therapeutic: 5dpi: n=3 vehicle, n=4 prophylactic, n=2. Data analyzed by 2-way ANOVA followed by Dunnett’s multiple comparisons. ‘*’ denotes p=0.0037 (prophylactic, 2dpi), 0.0365 (therapeutic, 2dpi). All error bars represent standard error about the mean.