Fig. 2. Anti-correlations are largely preserved across task and resting-state conditions.
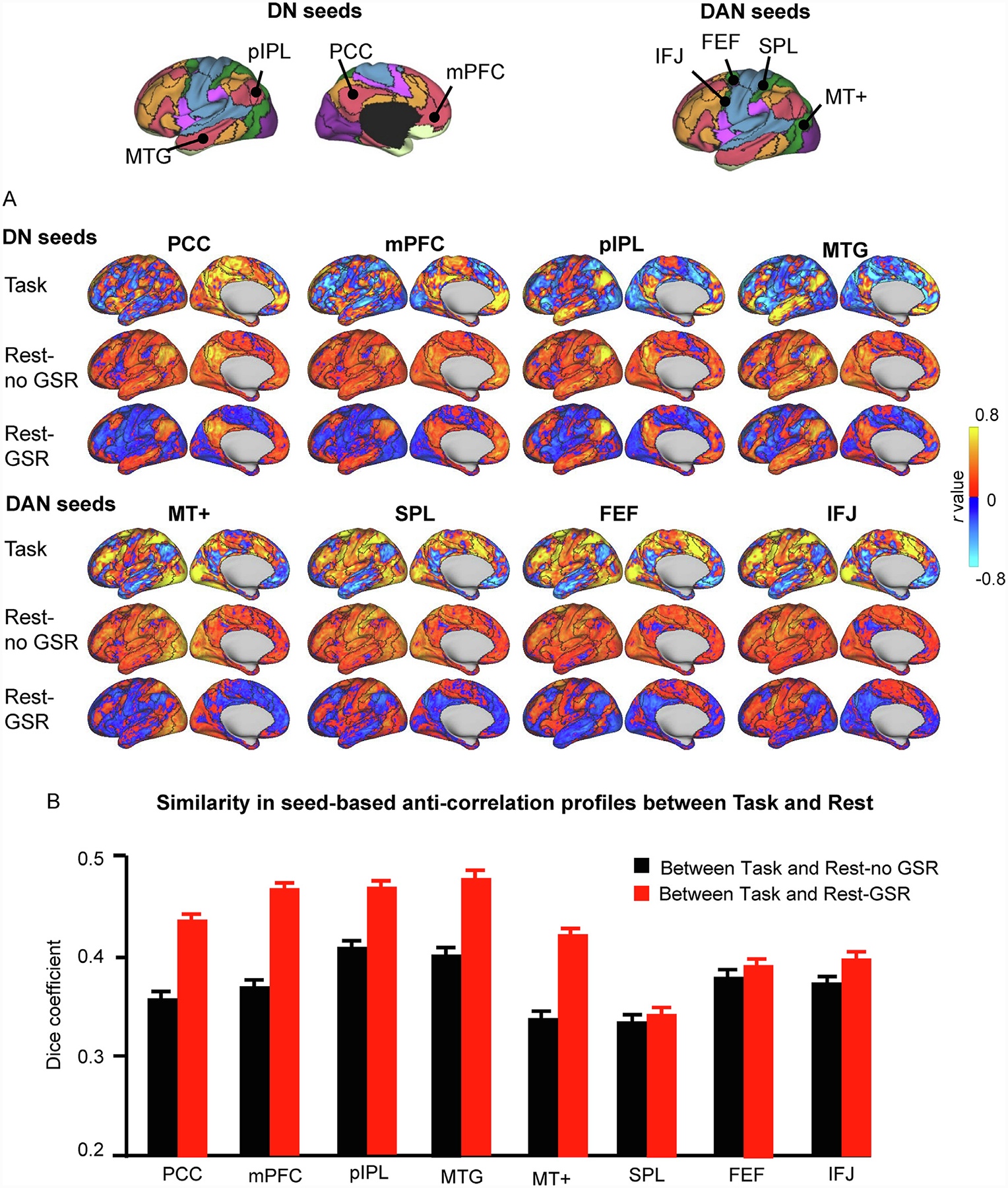
(A) Correlation maps from one participant (“784565″) were generated using seeds of the DN and DAN. The seeds are shown at the top of the figure, where black delineations indicate the boundaries of the 17-network parcellation and colors indicate the 7-network parcellation for easy identification of large-scale networks (Yeo et al., 2011). For each seed, we generated correlation maps (only the left cerebral hemisphere is shown) based on i) HCP task data, where task-evoked activity across the 47 task contrasts of the HCP database were concatenated (Task); ii) HCP resting-state data preprocessed without GSR (Rest-no GSR); and iii) HCP resting-state data preprocessed with GSR (Rest-GSR). The presence of anti-correlations across conditions, as well as their preserved spatial distribution, suggests that anti-correlations are meaningful and not simply spurious observations resulting from the GSR preprocessing step. The color scales illustrate r scores, whereby warm colors indicate positive correlations and cool colors indicate negative correlations. (B) Similarity in the seed-based anti-correlations between the Task and Rest-no GSR conditions (black bars) and between the Task and Rest-GSR conditions (red bars) across all participants. Similarity was quantified by calculating the Dice overlap coefficient between task-based and resting-state anti-correlations for each participant, and then averaged across participants. The Dice coefficients are greater for the Rest-GSR condition than for the Rest-no GSR condition (paired t-test, p<0.0001 for all seeds except for the SPL seed). Error bars represent standard errors.
DAN, dorsal attention network; DN, default network; PCC: posterior cingulate cortex; mPFC: medial prefrontal cortex; pIPL, posterior inferior parietal lobe; MTG: middle temporal gyrus; MT+: middle temporal region; SPL: superior parietal lobule; FEF: frontal eye field; IFJ: inferior frontal junction.
