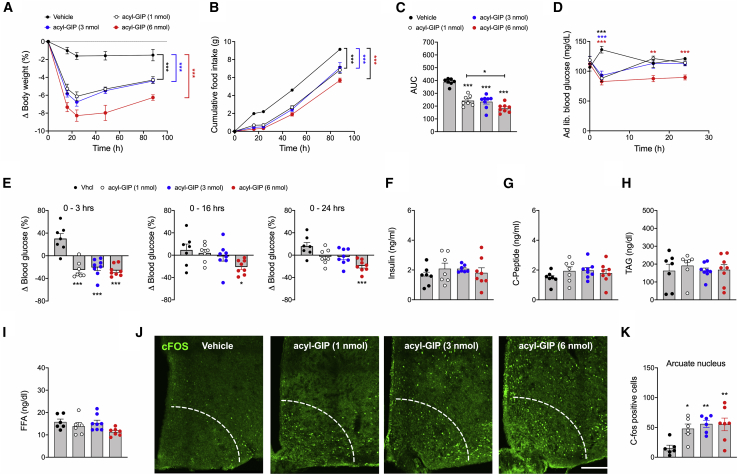
Figure 3.
Acute central administration of acyl-GIP improves body weight, food intake, and glycemia in DIO mice
(A–E) Body weight change (A), food intake (B and C), and plasma levels of blood glucose (D and E) in male DIO mice treated centrally (i.c.v.) with a single dose of 1, 3, or 6 nmol acyl-GIP (N = 7–8 mice each genotype).
(F–I) Ad libitum plasma levels of insulin (F) and c-peptide (G) and plasma levels of triglycerides (H) and free fatty acids (I) in 32-week-old DIO mice (N = 6–8 each group).
(J and K) cFOS immunofluorescence (J) and cFOS quantification (N = 6–7 mice each genotype) (K) in the hypothalamic arcuate nucleus (ARC) of DIO mice treated with acyl-GIP.
Data represent means ± SEM. ∗p < 0.05, ∗∗p < 0.01, and ∗∗∗p < 0.001. Scale bar, 100 μm. Longitudinal data (A, B, and D) were analyzed using two-way ANOVA with time and genotype as co-variables and Bonferroni post hoc analysis for individual time points. Bar graphs in (C), (E)–(I), and (K) were analyzed using one-way ANOVA.