Fig. 1.
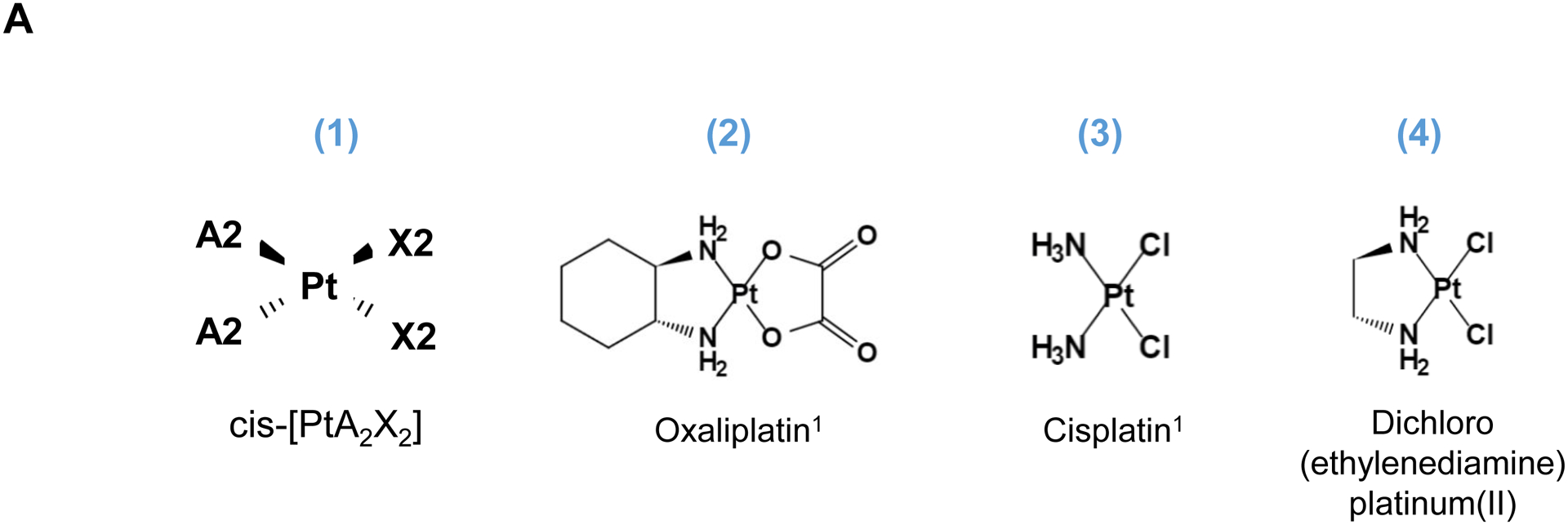
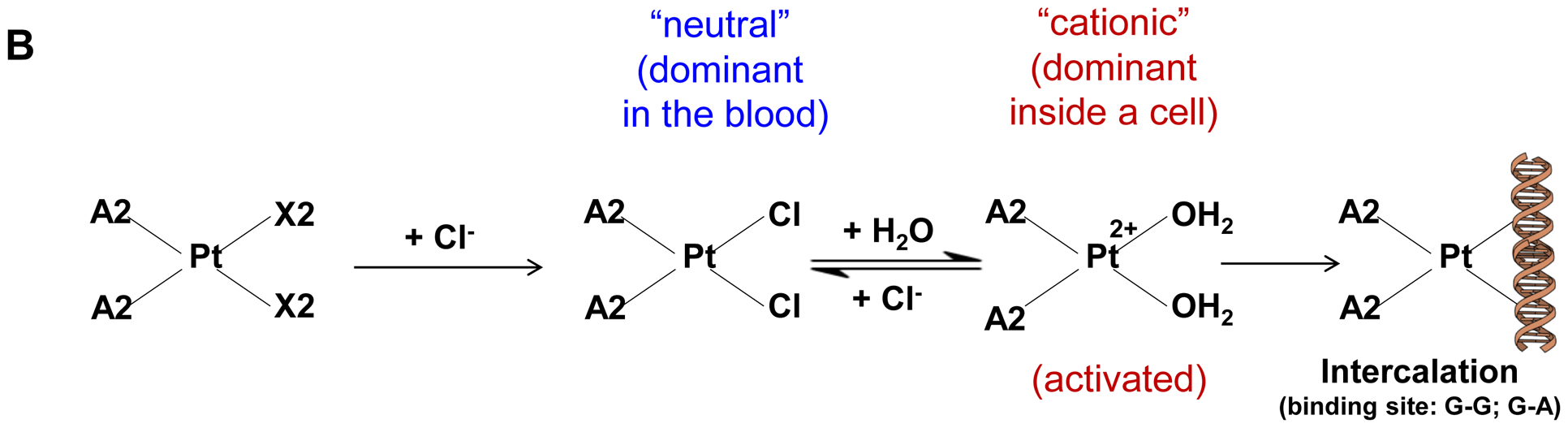
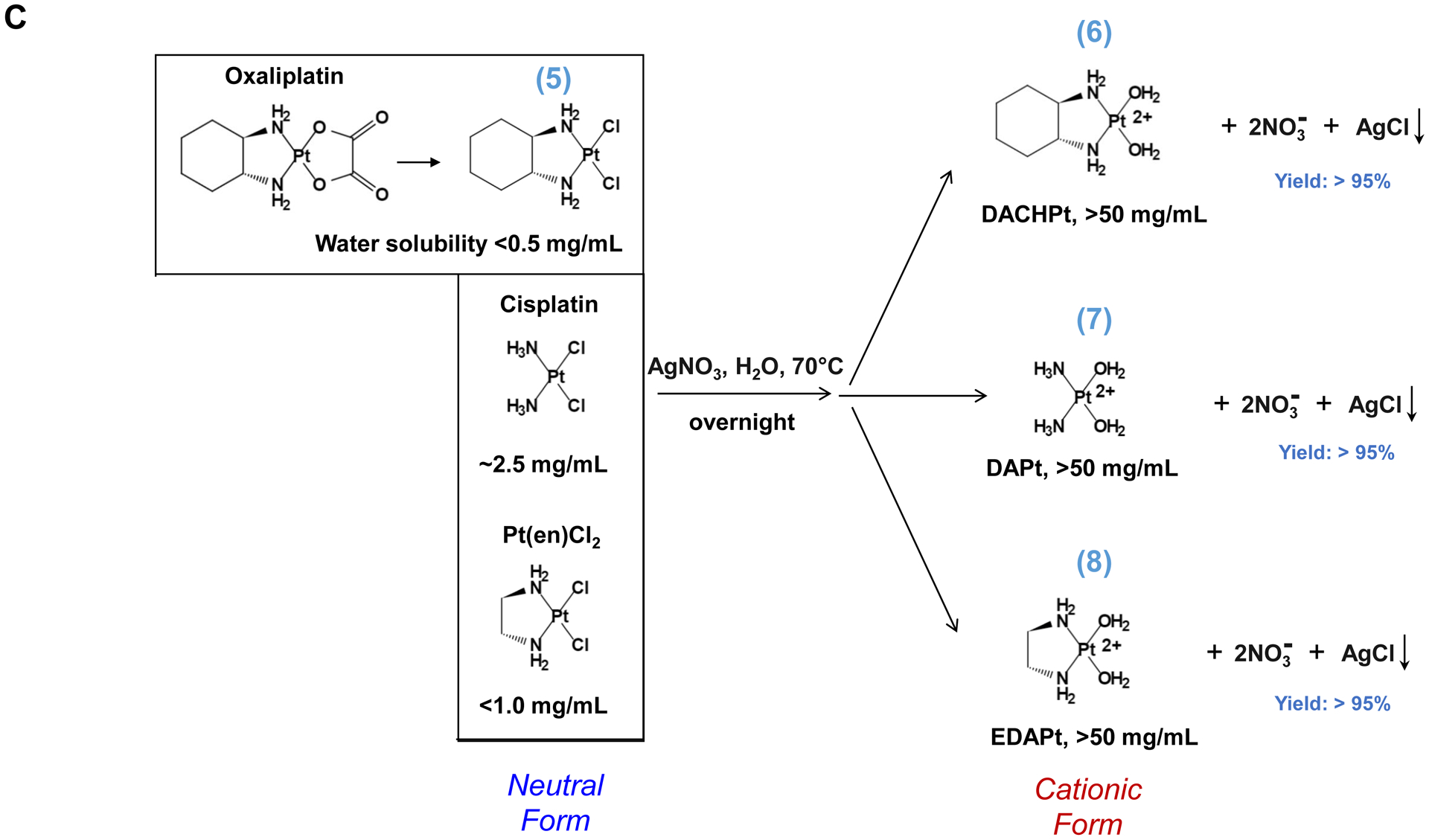
Synthesis of activated Pt drugs for the purpose of encapsulation by silicasomes. (A) Pt drugs are coordination compounds, with the basic structural composition of cis-[PtA2X2]. A2, i.e., two monodentate or one bidentate ligand with nitrogen donor atoms; X2: two monodentate or one bidentate anionic ligand(s). Representative Pt drugs studied in this project include oxaliplatin, cisplatin and Pt(en)Cl2. (B) Pt drugs in aqueous solution exist as equilibration species that can be depicted as “neutral” or “cationic”; the cationic variant is pharmaceutically active and capable of providing DNA cross linking. (C) Synthesis of cationic and active version of Pt drugs. This resulted in DACHPt (for oxaliplatin), DAPt (for cisplatin) and EDAPt (for Pt(en)Cl2), respectively. The yield of these reactions is high, i.e. ~95%.
