Fig. 4.
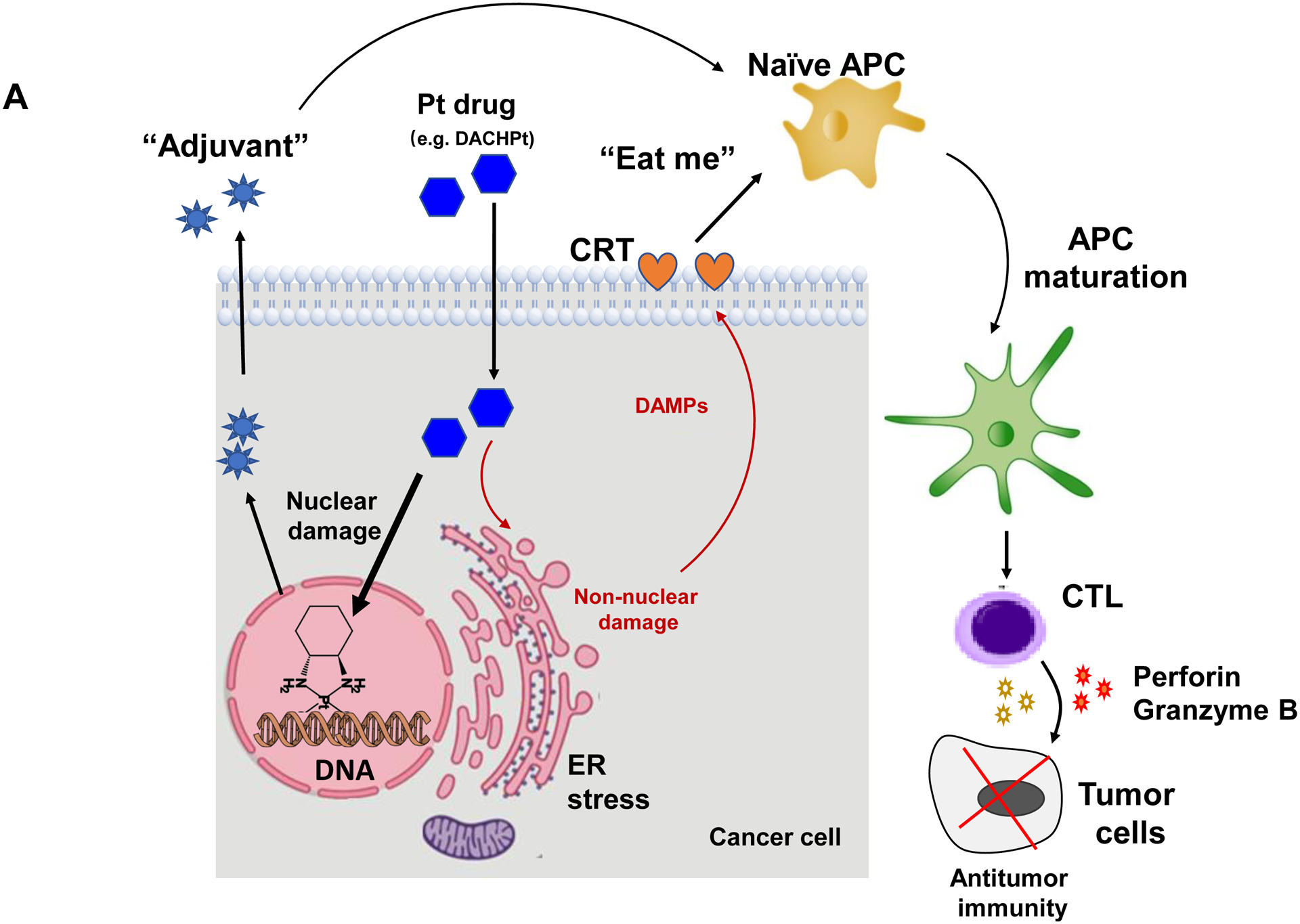
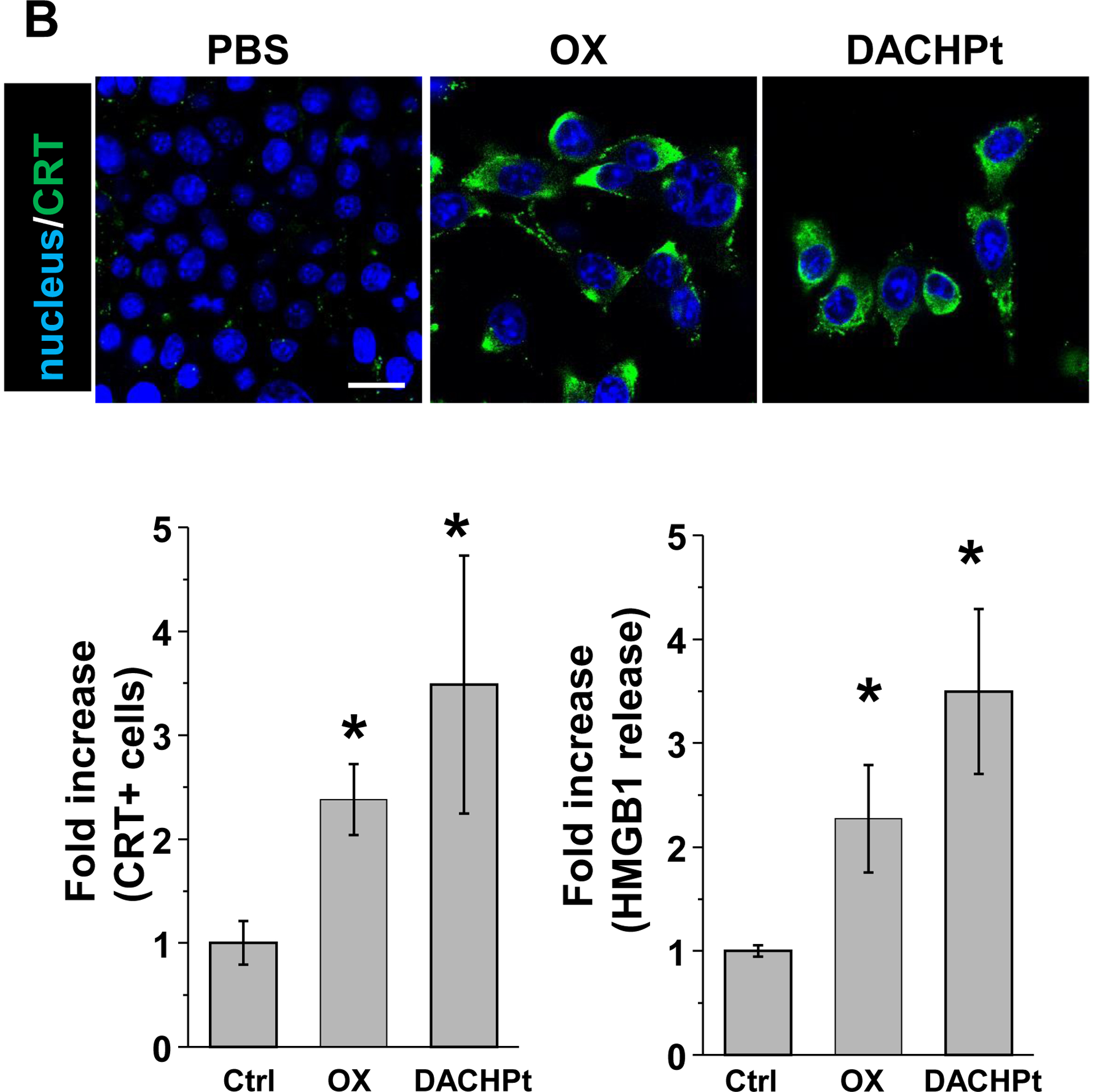
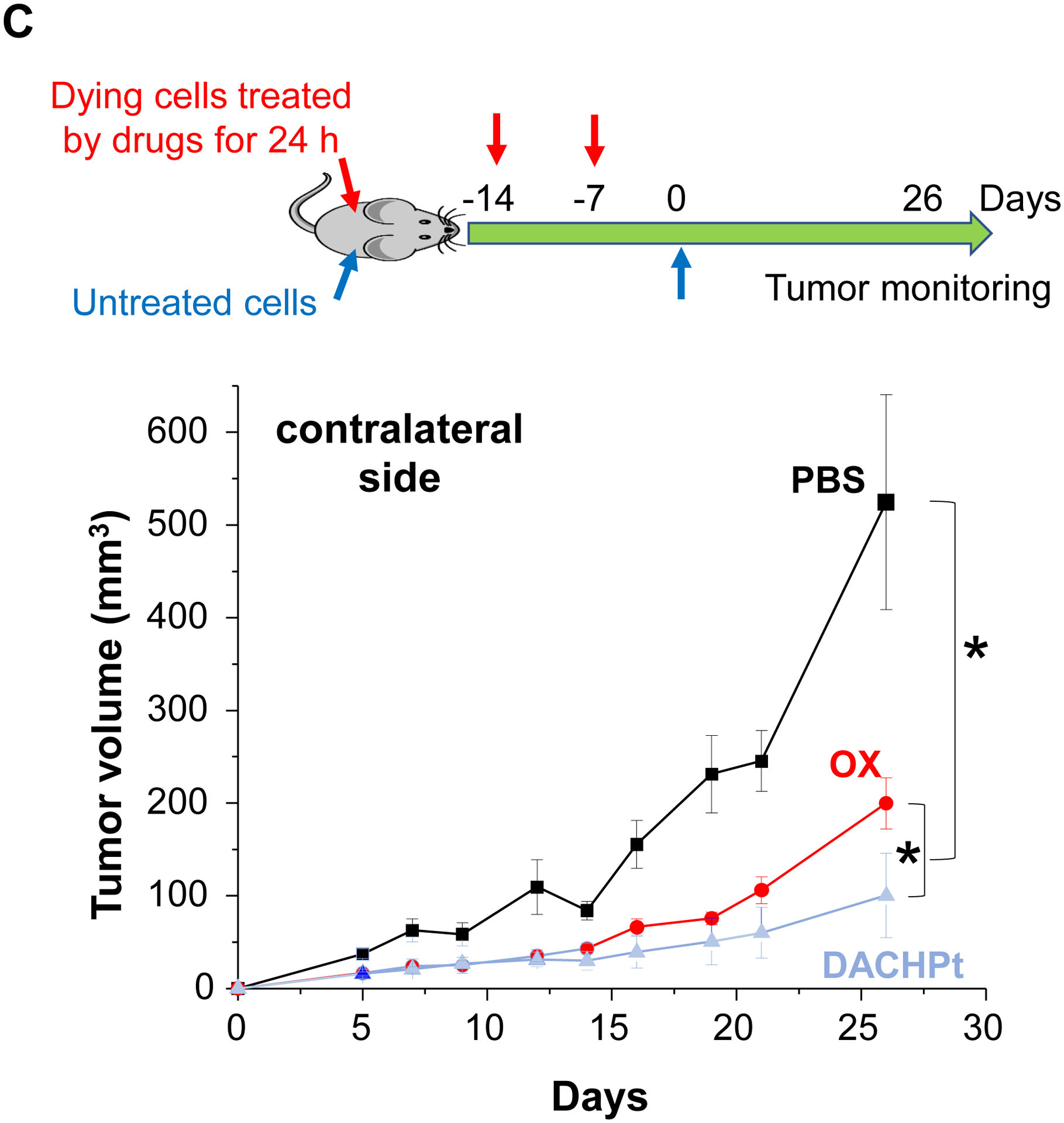
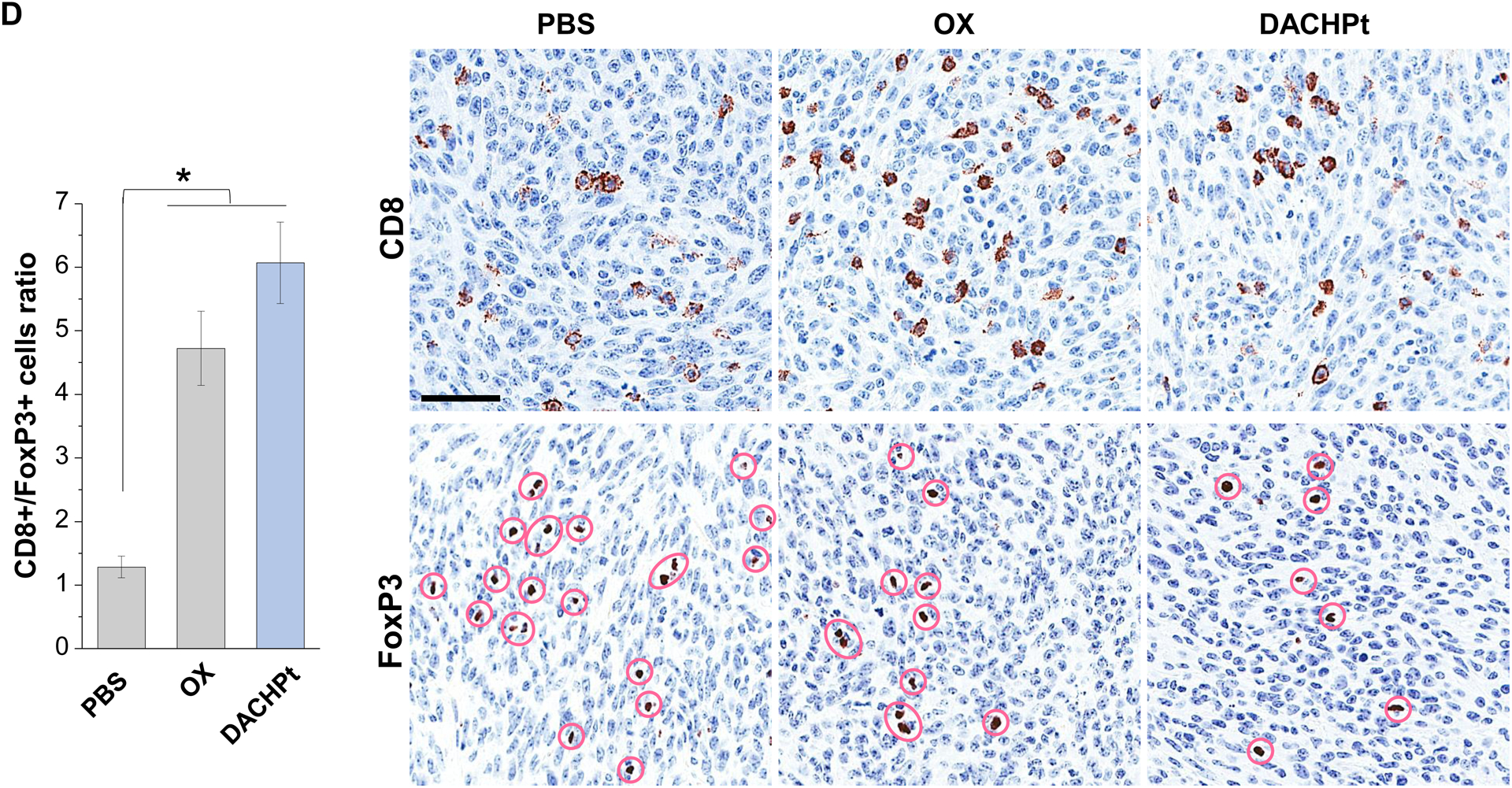
DACHPt induces immunogenic cell death (ICD) in the KPC tumor model. (A) Schematic to illustrate the action of DACHPt as an inducer of ICD. Select Pt chemo agents, such as DACHPt, induce and immunogenic response in which CRT expression on the dying cancer cell surface provides an “eat-me” signal for APC cells. The response is also accompanied by the release of adjuvant stimuli, such as HMGB1, which promote APC maturation and cross-presentation of endogenous tumor-associated antigens. This can lead to the activation and recruitment of CD8+ T cells capable of mediating cytotoxic cancer cell death by the release of perforin. (B) Upper panel: Confocal microscopy showing the appearance of CRT on the KPC cell surface treated with oxaliplatin or DACHPt (500 μM) for 24 h. Bar is 20 μm. Green: CRT; Blue: Nuclear. Lower panel: CRT expression was assessed by flow cytometer (left panel) and HMGB1 release was determined by ELSLA (right panel) in KPC cells exposed to oxaliplatin or DACHPt (500 μM) for 24 h. Data are expressed as mean ± SD, n=3. *, p < 0.05 compared to PBS control (one-way ANOVA followed by a Tukey’s test). (C) In vivo confirmation of the ICD effect by a vaccination study, in which healthy B6129SF1/J mice first received treatment with the chemo -induced dying KPC cells in one flank on two occasions one week apart, followed by injection of live KPC cells on the contralateral side. Tumors on the contralateral side were collected on day 26. (D) The tumor tissue was used for IHC analysis of CD8+ and Foxp3+ T cell appearance, allowing us to calculate a CD8+/Foxp3+ ratio. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM, n=6. *, p<0.05 (one-way ANOVA followed by a Tukey’s test). Bar is 50 μm.
