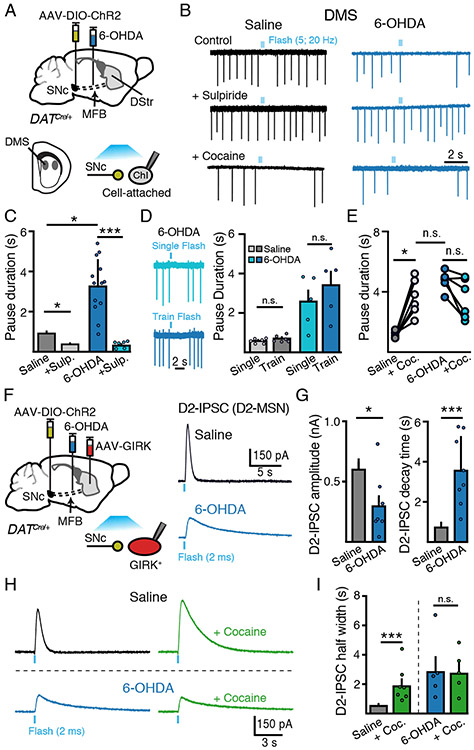
Figure 2. SNc dopamine-mediated inhibition of DMS Chi excitability is enhanced following partial dopamine loss.
(A) Schematic of MFB 6-OHDA and SNc AAV-DIO-ChR2 injections into DAT-Cre mice and recordings of DMS ChIs three weeks following.
(B) Cell attached recordings of DMS ChIs from control and low-dose 6-OHDA (1 μg/ μL) groups following optogenetic stimulation of dopamine inputs (5 flashes, 2 ms, 20 Hz). Sulpiride (500 nM) sensitive dopamine evoked pauses in DMS ChIs are enhanced following low-dose 6-OHDA.
(C) Quantification of the duration of SNc-evoked pause in ChI firing from (B). n = 6 - 15, N = 3 - 6.
(D) Representative traces from the same DMS ChI illustrating the effect of a single optogenetic stimulus (2 ms flash) and a train of stimuli (5 flashes, 2 ms, 20 Hz) and quantification of the duration of SNc-evoked pause in ChI firing.
(E) Lack of effect of cocaine (3 μM) on SNc-evoked pauses following 6-OHDA. n = 6. N = 2.
(F) Schematic of viral injections of MFB 6-OHDA, SNc AAV-DIO-ChR2 and striatal AAV-tdTomato-GIRK2 injection into DAT-Cre mice and recordings of GIRK2 mediated D2-IPSCs in D2-MSNs evoked by optogenetic stimulation of dopamine inputs three weeks following.
(G) Summary of amplitude and decay time of D2-IPSCs from D2-MSNs in control and low-dose 6-OHDA (1 μg/ μL) groups. n = 6 - 8, N = 4 - 8.
(H) Representative traces of D2-MSN D2-IPSCs illustrating the effect of cocaine (3 μM) on the duration of D2-IPSCs in saline and 6-OHDA injected animals.
(I) Quantification of D2-IPSC half-width time from (H). n = 5 - 9, N = 4.
Summary data are mean ± SEM. * = p < 0.05, ** = p < 0.01, *** = p < 0.001, n.s. = p > 0.05.