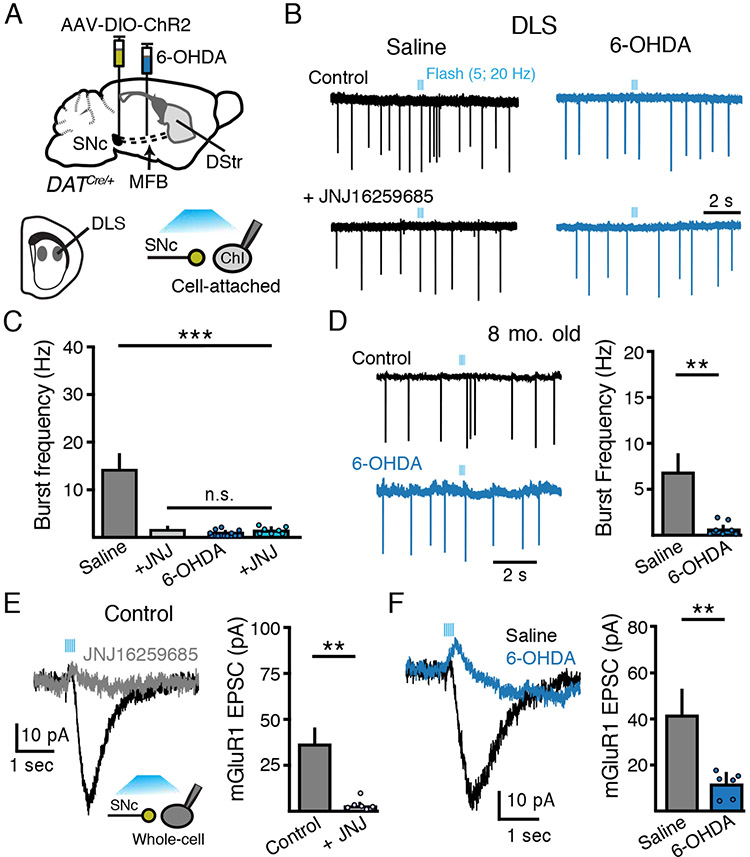
Figure 3. SNc glutamate corelease-evoked bursting of DLS ChIs is lost following partial dopamine loss.
(A) Schematic of MFB 6-OHDA and SNc AAV-DIO-ChR2 injections into DAT-Cre mice and recordings from DLS ChIs three weeks following.
(B) Cell attached recordings of DLS ChIs from control and low-dose 6-OHDA (1 μg/ μL) groups following optogenetic stimulation of dopamine inputs (5 flashes, 2 ms, 20 Hz). JNJ16259685 (20 μM) sensitive burst firing is abolished following low-dose 6-OHDA.
(C) Quantification of SNc-evoked ChI burst frequency in DLS ChIs firing from (B). n = 7 - 14, N = 2 - 4.
(D) Representative traces and quantification of DLS ChI burst firing following photoactivation of SNc inputs from saline or low-dose 6-OHDA treated 8-month-old mice. n = 6 - 7, N = 3.
(E) Representative trace and amplitude quantification of SNc-evoked (5 flashes, 2 ms, 20 Hz) JNJ16259685 (20 μM) sensitive mGluR EPSCs. n = 6, N = 2.
(F) Optogenetic stimulation evoked mGluR-mediated EPSCs from DLS ChIs are abolished following 6-OHDA. Right: summary of mGluR-mediated EPSCs in DLS ChIs from saline and 6-OHDA groups. n = 6 – 7, N = 3.
Summary data are mean ± SEM. ** = p < 0.01, n.s. = p > 0.05.