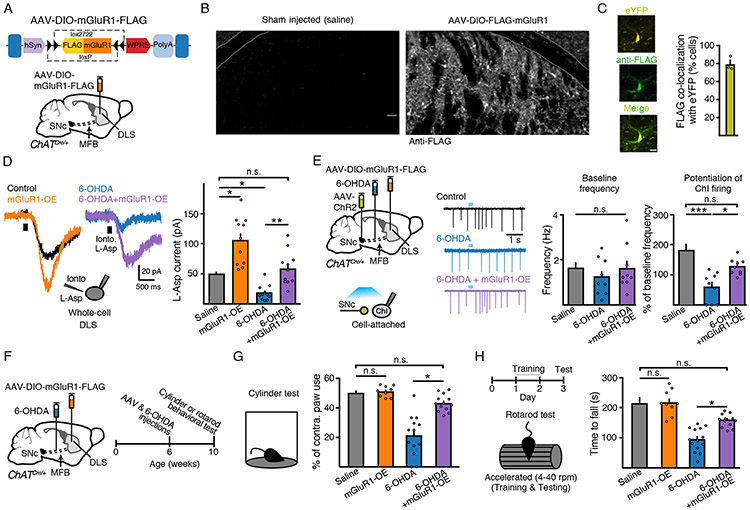
Figure 6. Overexpression of mGluR1s rescues parkinsonian circuit and motor deficits.
(A) Schematic of design and injection of AAV-DIO-mGluR1-FLAG in ChAT-Cre mice.
(B) Immunohistochemical images illustrating anti-FLAG immunoreactivity from saline and AAV-DIO-mGluR1-FLAG injected hemispheres in ChAT-Cre mice.
(C) eYFP and FLAG co-localization IHC images and quantification following AAV-DIO-eYFP and AAV-DIO-mGluR1-FLAG co-injection into the DLS of ChAT-Cre mice. Scale bar = 25 μm. N = 3.
(D) L-aspartate (200 nM, 500 ms) evoked mGluR mediated inward currents. mGluR overexpression rescues 6-OHDA-induced loss of current amplitude. n = 11 - 12, N = 2 - 3.
(E) Schematic of MFB saline or 6-OHDA, midbrain AAV-ChR2 and striatal AAV-DIO-mGluR1-FLAG injections into ChAT-Cre mice and recordings from ChIs three weeks following. Representative traces and quantification of baseline firing and ChR2 evoked DLS ChI bursting and rescue in 6-OHDA + mGluR1 overexpressing mice. n = 9 - 10, N = 3.
(F) Schematic and timeline of injections and cylinder or rotarod behavioral tests.
(G) Contralateral paw use in cylinder behavioral test. N = 9 – 14.
(H) Latency to fall on test day (day 3) on rotarod (4 - 40 rpm). N = 6 - 14.
Summary data are mean ± SEM. ** = p < 0.01, *** = p < 0.001, n.s. = p > 0.05