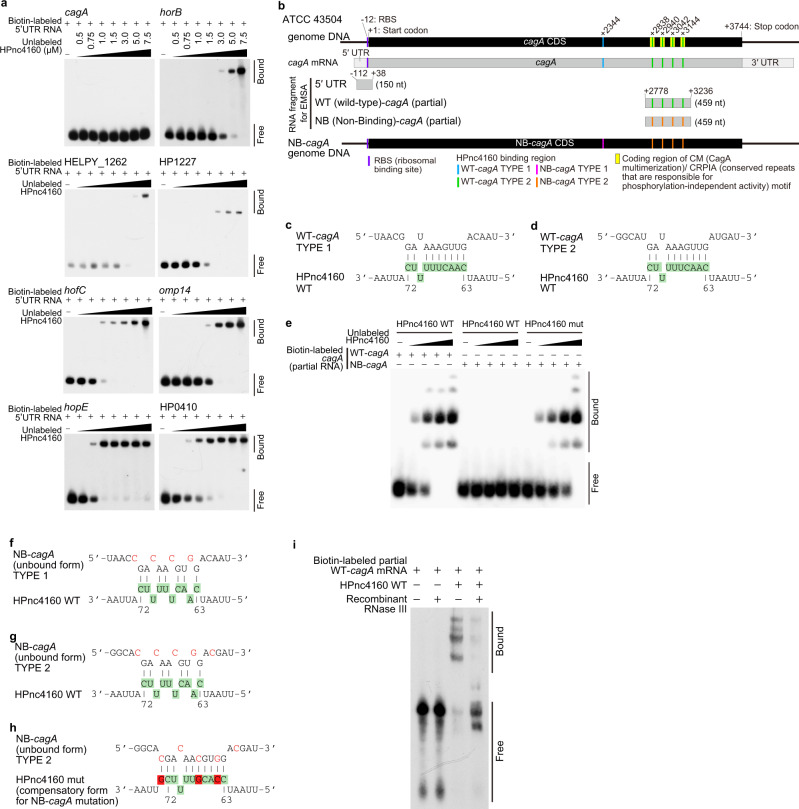
Fig. 3. HPnc4160 binds to target mRNA.
a Electrophoretic mobility shift assay (EMSA) analysis of HPnc4160 binding to the 5′UTR region of each candidate mRNA. Data are representative of two independent experiments. b Schematic of CagA motifs, HPnc4160 binding regions, and HPnc4160-non-binding cagA (NB-cagA). c, d Schematic of predicted HPnc4160 binding sites in the corresponding CDS sequence of cagA TYPE 1 (c) and TYPE 2 (d). Upper sequences indicate target cagA mRNA sequences; lower sequences indicate the HPnc4160 sequence with base numbers. Colored sequences correspond to the loop structures indicated in Supplementary Fig. 4a. e EMSA analysis of HPnc4160 WT or HPnc4160 mut (a compensatory form of NB-cagA) bindings to RNA of partial cagA WT or NB-cagA. Data are representative of two independent experiments. f–h Schematic of CDS sequence of the NB-cagA of TYPE 1 (f) and TYPE 2 (g) and HPnc4160 mut (h). Upper sequences indicate target cagA mRNA sequences; lower sequences indicate the HPnc4160 sequence with base numbers. Green-colored sequences correspond to the loop structures of HPnc4160 indicated in Supplementary Fig. 4a. Mutated nucleotides in the cagA mRNA sequence are shown in red. Red-colored sequence correspond to mutated nucleotides in the hpnc4160 sequence (h). i RNase protection assay with HPnc4160, cagA mRNA, and recombinant RNase III. Data are representative of two independent experiments. Source data are provided as a Source Data file.