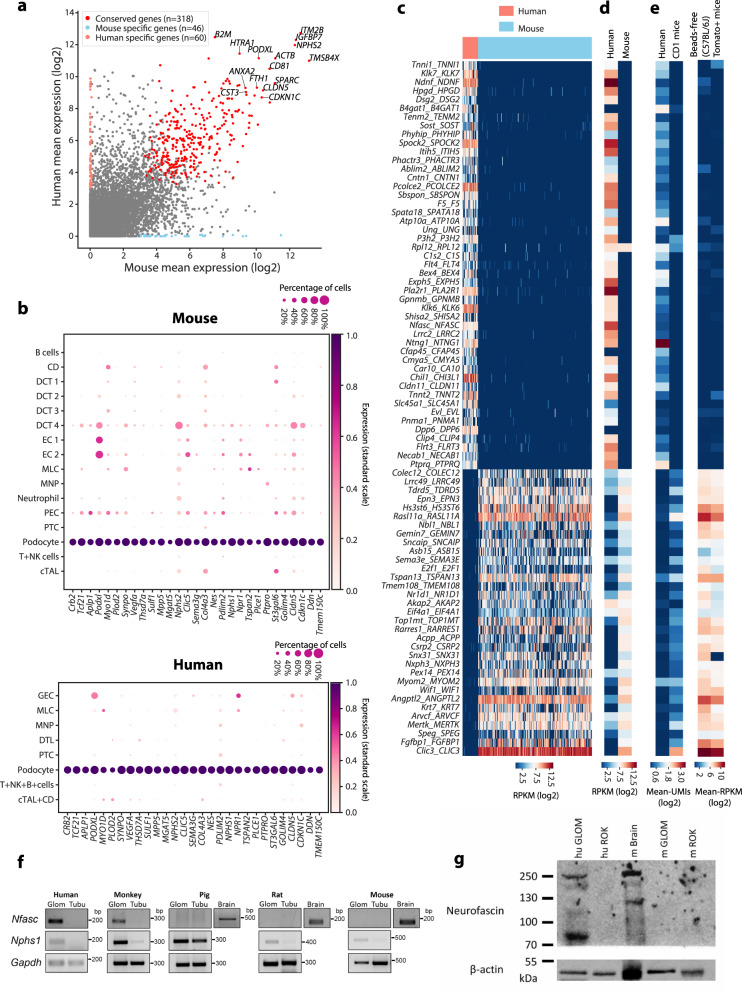
Fig. 5. Differential and conserved podocyte gene expression profile between mouse and human.
a The expression (mean log2-transformed RPKM) of mouse and human gene homologues in podocytes. Human- (n = 60) and mouse-specific (n = 46) genes are indicated in salmon and light blue, respectively. Conserved genes highly expressed in both species (n = 318) are indicated in red. Detailed information can be found in Supplementary Data 9. b The expression of conserved podocyte highly expressing genes in identified cell types in mouse (C57BL/6J) (upper panel) and human (lower panel). The colour intensity and size of each dot represents the mean expression (standard scale) and the percentage of cells expressing each gene in individual cell types, respectively. c Heatmap showing the levels of differentially expressed genes in podocytes between mouse and human. The colour scale is defined by log2(mean RPKM). d In silico validation of podocyte species-specific genes using published bulk podocyte RNA-seq data from mouse and human. The expression levels are shown as log2-transformed RPKM. e In silico validation of podocyte species-specific genes using published (left) and in-house (right) scRNA-seq data of annotated human and mouse podocytes. Expression levels are shown as log2-scale average UMI counts (published data) and as log2-scale average RPKM (in-house data). f Experimental validation for the gene expression of human-specific gene NFASC. RT-PCR was used to detect the expression of Nfasc in kidney fractions (glom: glomerulus, tubu: tubule) isolated from human, cynomolgus monkey, minipig, rat and mouse. Nphs1 and Gapdh were used as loading controls. cDNA generated from the brain tissue served as an experimental positive control. The molecular-weight size of PCR amplicons is indicated in the right side as bp. g Western blot analysis of NFASC in mouse and human glomeruli. Lysates of human and mouse glomeruli (hu GLOM, m GLOM) and tubules (hu ROK, m ROK, glomerulus-free or rest of kidney) were used. As a positive control, the mouse brain lysate (m Brain) was used. β-actin was used as a loading control. Protein molecular mass (kDa) is shown on the left side of the blot image. Of note, the blots for NFACS and β-actin were derived from the same Western blot, but were treated separately for the exposure processes due to notably weaker signal for NFASC than β-actin. The original raw data for blots and PCR gel images are available in the Source data file.