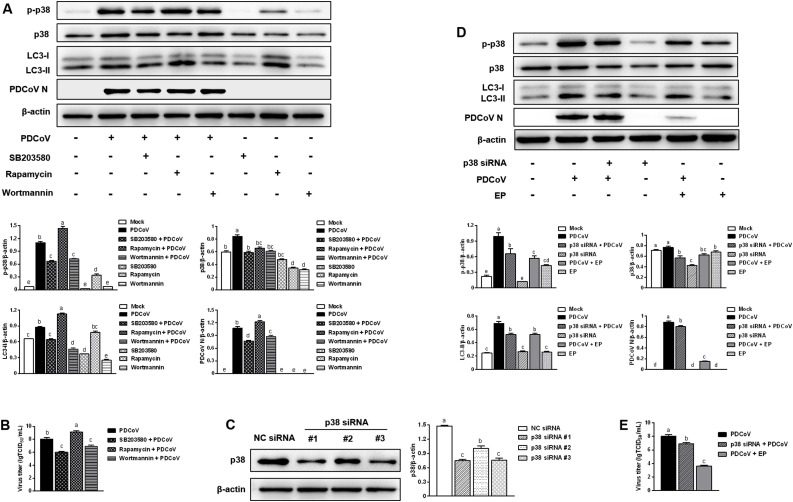
Fig. 5.
The p38 signaling pathway participates in the inhibition of EP on PDCoV-induced autophagy. (A) LLC-PK1 cells were pretreated with p38 inhibitor SB203580 (5 μM), rapamycin (62.5 μg/mL) or wortmannin (5 μg/mL) prior to PDCoV infection (MOI = 2). After PDCoV adsorption for 1 h, the cells were further cultured in fresh medium in the absence or presence of SB203580 (5 μM), rapamycin (31.2 μg/mL) or wortmannin (2.5 μg/mL). The expressions of p-p38, p38, LC3-II and PDCoV N were analyzed by western blot at 24 hpi. Results were presented as the ratio of target protein band intensity to β-actin band intensity. (B) The virus titer (lgTCID50/mL) in LLC-PK1 supernatants was calculated by the method of Reed and Muench. (C) The efficiency of p38 siRNA was evaluated by western blot. LLC-PK1 cells were transfected with the indicated siRNA. At 24 h post transfection, the expression of p38 was analyzed by western blot. Results were presented as the ratio of p38 band intensity to β-actin band intensity. (D) LLC-PK1 cells were transfected with p38 siRNA #1 or NC siRNA. At 24 h post transfection, the cells were mock-infected or infected with PDCoV (MOI=2) in the absence or presence EP (150 μM). After PDCoV adsorption for 1 h, the cells were further cultured in fresh medium in the absence or presence EP (150 μM). The expressions of p-p38, p38, LC3-II and PDCoV N were analyzed by western blot at 24 hpi. Results were presented as the ratio of target protein band intensity to β-actin band intensity. Values represent the mean ± SEM for three independent experiments. Mean values without a common superscript (a, b, c, d, e) differ significantly (P < 0.05).