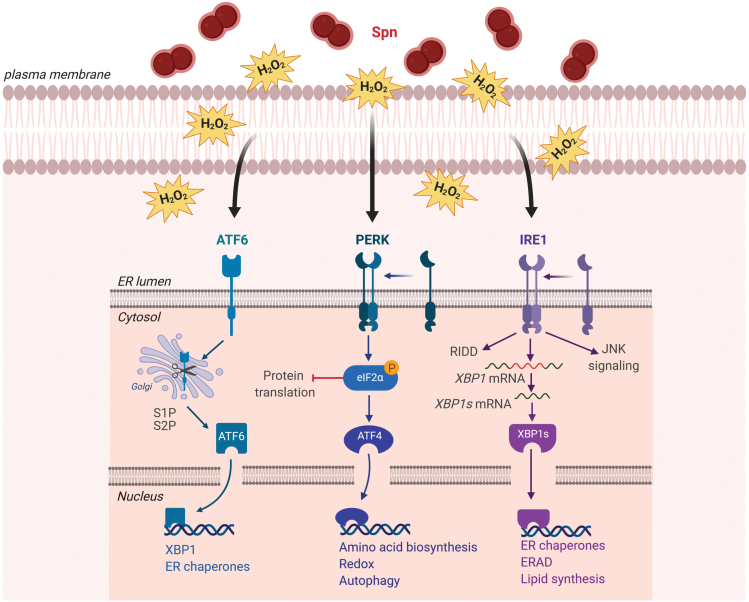
FIG. 2.
Actions of Spn-derived H2O2 on the UPR in host cells. Infection with Spn induces the activation of the UPR. Secretion of Spn-derived H2O2 leads to activation of PERK, ATF-6, and IRE1. Dimerization and phosphorylation of activated PERK induce phosphorylation of eIF2α leading to inhibition of protein translation and ATF4 modulating expression of target genes. Activated ATF-6 translocates to the Golgi, where it is cleaved by S1P and S2P. The processed ATF-6 enters the nucleus acting as a transcription factor of target genes. Activation of IRE1 leads to splicing of xbp1 mRNA, which acts as transcription factor of target genes. IRE1 activation can also lead to RIDD of mRNA or JNK signaling activation. ATF4, activating transcription factor 4; ATF6, activating transcription factor 6; eIF2α, eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2α; ER, endoplasmic reticulum; IRE1, inositol-requiring enzyme 1; JNK, c-Jun N-terminal kinase; PERK, protein kinase R (PKR)-like ER kinase; RIDD, regulated IRE1-dependend decay; S1P, site-1-protease; S2P, site-1-protease; Spn, Streptococcus pneumonia; UPR, unfolded protein response; xbp1, X-box-binding protein 1. Color images are available online.