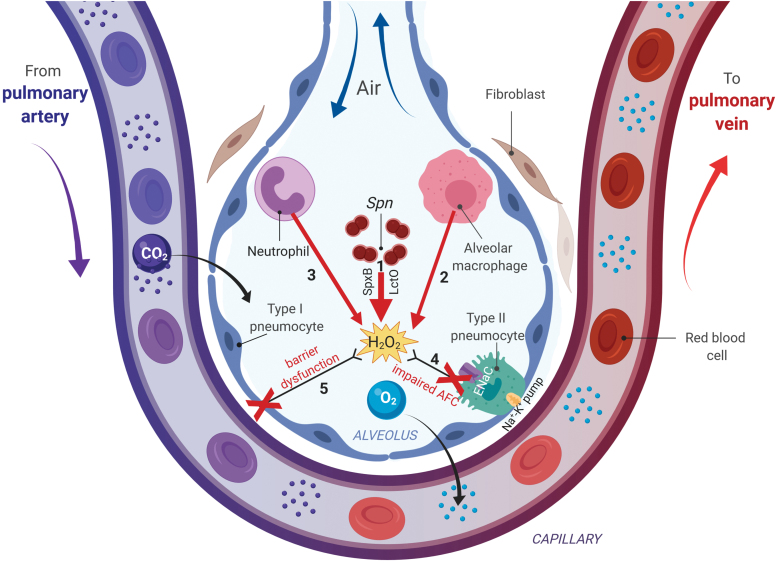
FIG. 4.
The complex actions of H2O2 in alveoli during pneumococcal pneumonia. Spn will migrate into the lower respiratory tract, and since it lacks catalase will generate millimolar levels of H2O2, through the actions of pyruvate oxidase (SpxB) and lactate oxidase (LctO), which will diffuse into the alveolar space (1). Moreover, an early neutrophil-mediated and a later macrophage-derived generation and secretion of μmolar levels of H2O2 will occur (2, 3). High ROS levels in the alveolar space will promote alveolar endothelial barrier function (4) and will impair AFC (5), which is mainly mediated through vectorial sodium transport, involving the apically expressed ENaC and the basolateral Na+-K+ pump in type II pneumocytes. AFC, alveolar fluid clearance; ENaC, epithelial sodium channel; ROS, reactive oxygen species. Color images are available online.