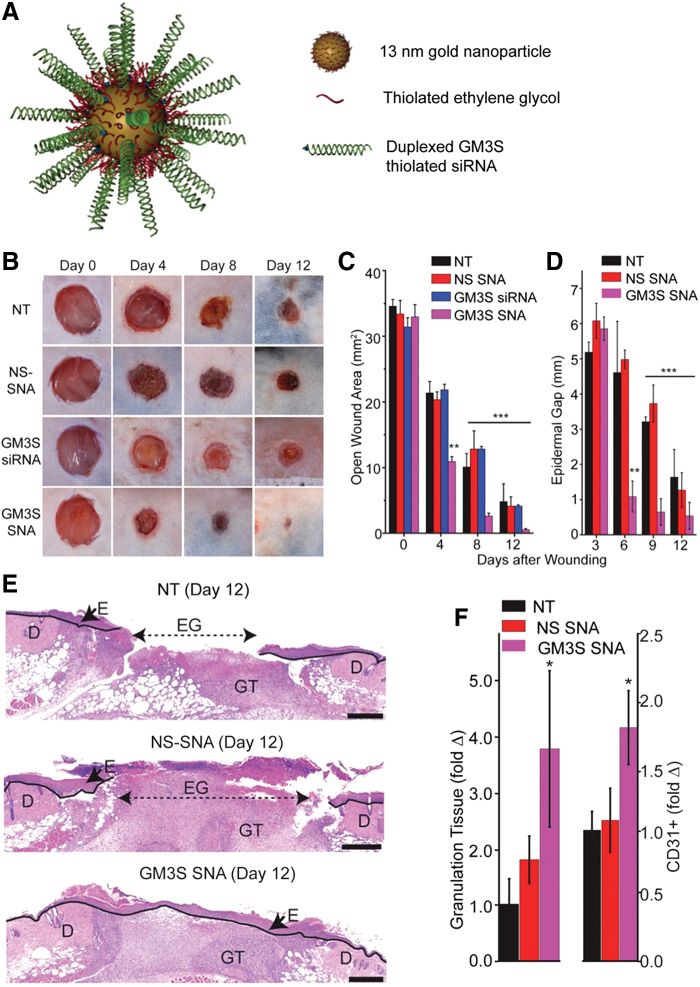
Figure 3.
The topical administration of AuNPs conjugated to spherical nucleic acid for GM3S shows a reduction in local GM3S expression and heals the wound in 12 days in diabetic mice wounds. An increase in granulation tissue, new blood vessel formation, and IGF-1 and EGF receptor phosphorylation is observed. (A) SNA are 13-nm gold cores functionalized with thiolated siRNA duplexes (targeted to) and oligoethylene glycol for colloidal stability. (B–E) Topical application of GM3S SNA prevents the delayed wound healing in the DIO mouse. (B) Representative clinical images of wounds. (C) Computerized measurements of the open wound area. (D) Epidermal gap (the maximum distance between KCs at the leading wound edges) was measured by computerized morphometry. (E) Representative histologic images of NT and NS SNA- and GM3S SNA-treated wounds at day 12. D, dermis; E, epidermis; EG, epidermal gap; GT, granulation tissue (Scale bar: 500 μm.). (F) Granulation tissue area and vascularity (CD31+ staining) of the diabetic wounds. Adapted from 55 with permission. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001. AuNPs, gold nanoparticles; EGF, epidermal growth factor; GM3S, ganglioside-monosialic acid 3 synthase; IGF-1, insulin-like growth factor-1. Color images are available online.