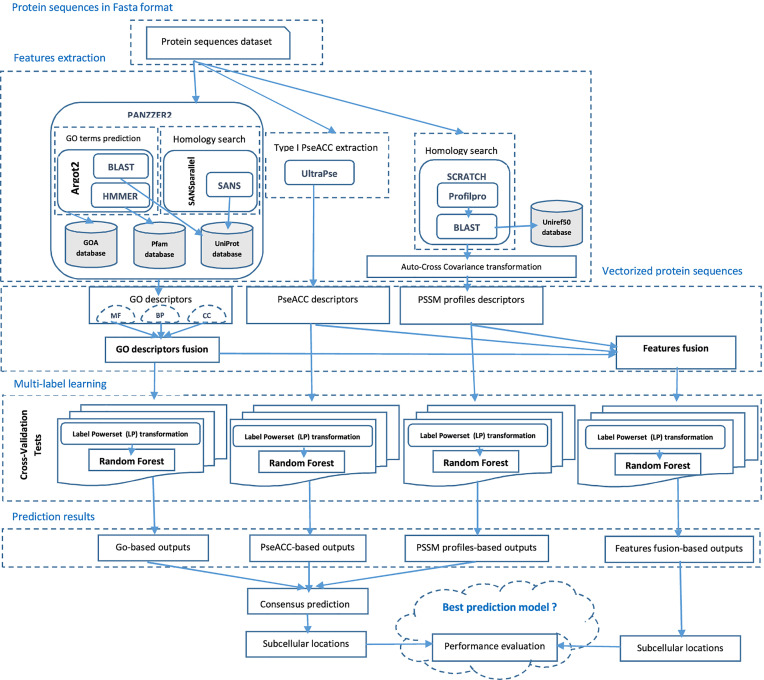
Figure 1:
Flowchart for the proposed prediction model for Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacterial proteins subcellular localization. Firstly, protein sequences datasets were collected from the published database. Secondly, they were filtered out and preprocessed using different strategies to obtain a fixed size feature vector representation that can be fed into the learning model. Thirdly, the resulting encoded feature vectors were independently put into the multi-label learning model-based on Label Powerset (LP) transformation to produce independent prediction scores using Random Forest (RF) ensemble method as base classifier. Once optimum performance scores were calculated by using 5-fold cross-validation tests, the final prediction model is built.