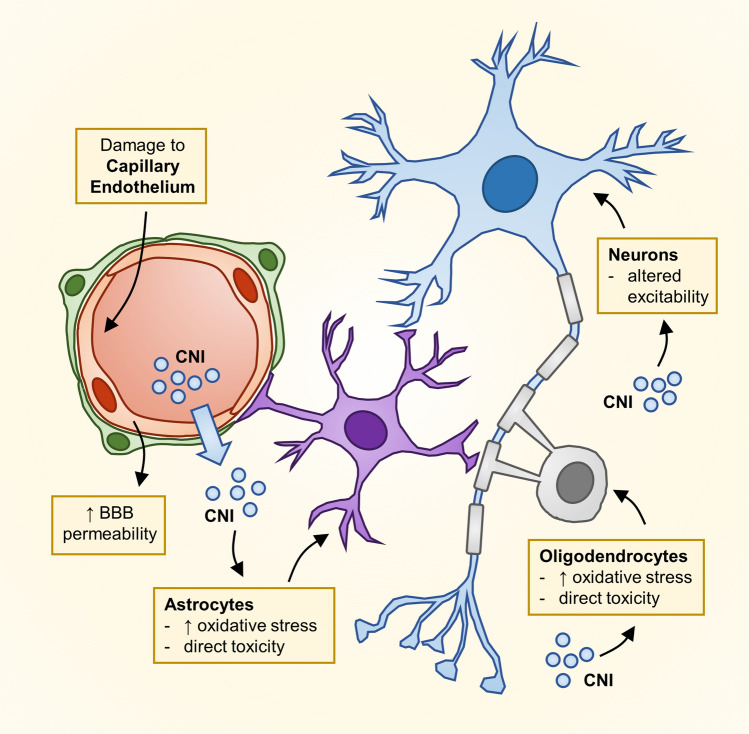
Fig. 2.
Proposed mechanisms of neural toxicity due to calcineurin inhibitors (CNIs). Blood–brain barrier (BBB) permeability can be altered by CNI-induced damage to the capillary endothelium or by other concomitant disorders (e.g. infection and inflammation). CNI crossing of the damaged BBB may lead to altered neuronal excitability and could result in direct toxicity on glial cells (astrocytes and oligodendrocytes), which are particularly susceptible to these agents due to their high calcineurin content