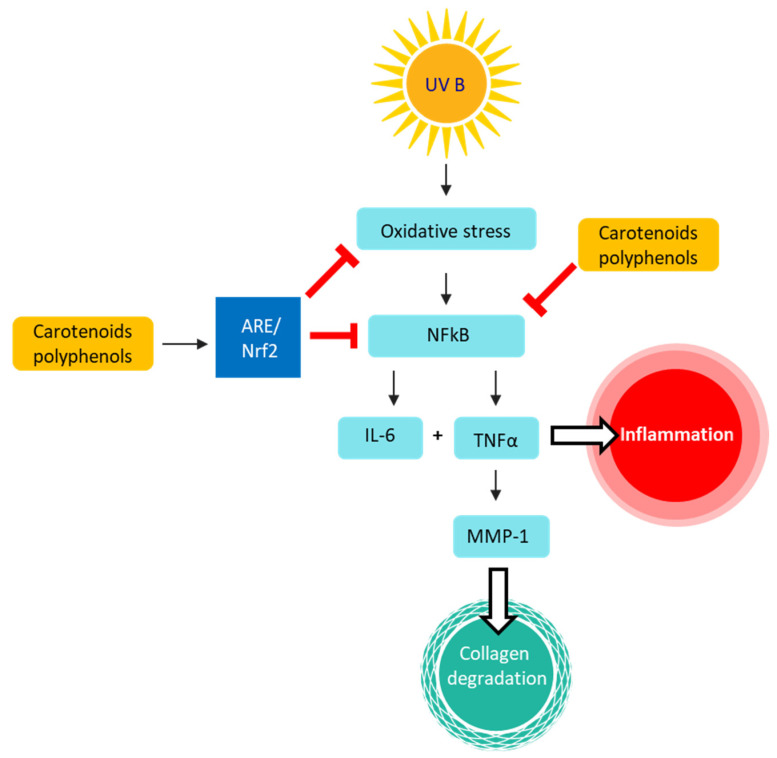
Scheme 1.
A model summarizing the suggested role of the studied parameters in the skin-damaging effects of UV irradiation. UVB irradiation causes oxidative stress and leads to activation of the NFκB transcription system, which results in induction of various inflammatory cytokines including IL-6 and TNFα. These cytokines lead to skin inflammatory responses such as erythema. TNFα induces the expression of MMP-1, which leads to collagen degradation and to decreased skin elasticity. Carotenoids and polyphenols inhibit NFκB and induce ARE/Nrf2. Activation of the ARE/Nrf2 transcription system by phytonutrient combinations can reduce UV-induced oxidative stress, which may partially explain the attenuation of UV-induced adverse effects.