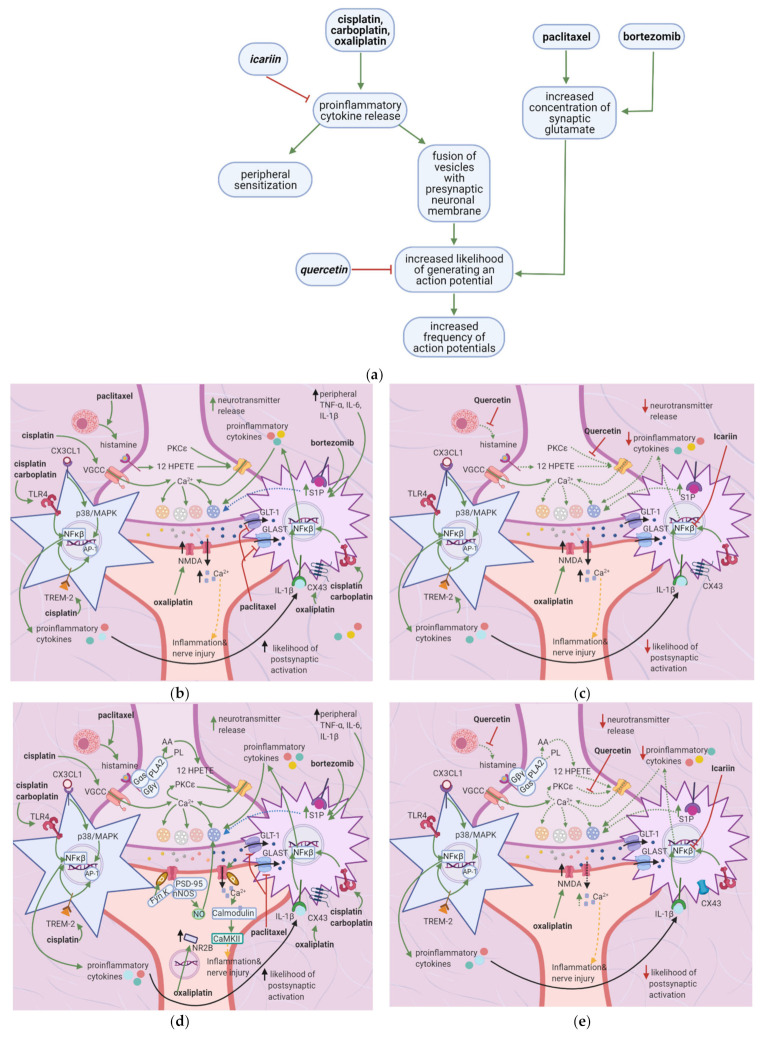
Figure 5.
Anticancer drugs modulate signal transmission at a synapse in the dorsal horn spinal cord, and flavonoids counter these effects; (a) Simplified Overview of how flavonoids counter the effects of anticancer drugs at the spinal cord dorsal horn. (b) Actions of anticancer drugs at the spinal cord dorsal horn. Anticancer drugs increase presynaptic NT release and the likelihood of postsynaptic neuronal activation and activate microglial cells and astrocytes, releasing proinflammatory cytokines. Proinflammatory cytokines increase glutamate release and sensitize primary afferent channels; (c) Flavonoids counteract anticancer drugs’ actions at the dorsal horn by inhibiting mast cell degranulation, PKC epsilon translocation, and NF-κB activation. This decreases the likelihood of postsynaptic action potential generation; (d) Anticancer drugs increase intracellular Ca2+ at the synaptic terminal in DRG neurons via activation of VGCC and histamine release, which leads to TRPV1 sensitization; (e) Flavonoids reduce neuropathic pain by inhibiting mast cell degranulation. Thus, histamine release and H1R activation decrease, eventually leading to decreased NT release.