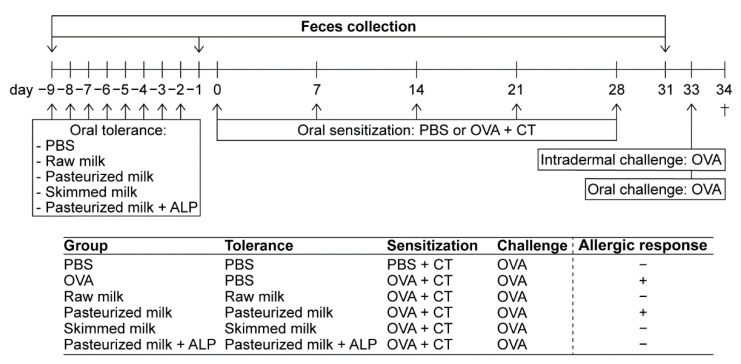
Figure 1.
Schematic overview of the study design. Female C3H/HeOuJ mice were grouped as depicted: PBS (PBS-sensitized control mice; n = 6), OVA (OVA-sensitized allergic mice; n = 8), raw milk (raw milk-treated mice; n = 8), pasteurized milk (pasteurized milk-treated mice; n = 8), skimmed milk (skimmed raw milk-treated mice; n = 8), and pasteurized milk + ALP (pasteurized milk + ALP-treated mice; n = 8). On experimental days 0, 7, 14, 21, and 28, mice were orally sensitized to the hen’s egg protein OVA using cholera toxin as an adjuvant (20 mg of OVA + 10 µg of CT/0.5 mL of PBS). PBS-sensitized control mice received cholera toxin alone. Prior to sensitization, mice were orally treated with 0.5 mL of PBS (as a control), raw milk, pasteurized milk, skimmed raw milk, or pasteurized milk supplemented with ALP for eight consecutive days (day −9 to −2). On days −9, −1, and 31 (before tolerance induction, after tolerance induction, and after sensitization), fecal samples were collected for microbiota analysis. On day 33, all mice were intradermally (10 µg of OVA/20 µL of PBS) and orally (50 mg of OVA/0.5 mL of PBS) challenged with OVA. Mice were killed on day 34 (as indicated by †). The allergic response in each group is displayed with a “+” for an allergic response or a “–” for no allergic response (results previously published [22]). PBS, phosphate-buffered saline; ALP, alkaline phosphatase; OVA, ovalbumin; CT, cholera toxin.