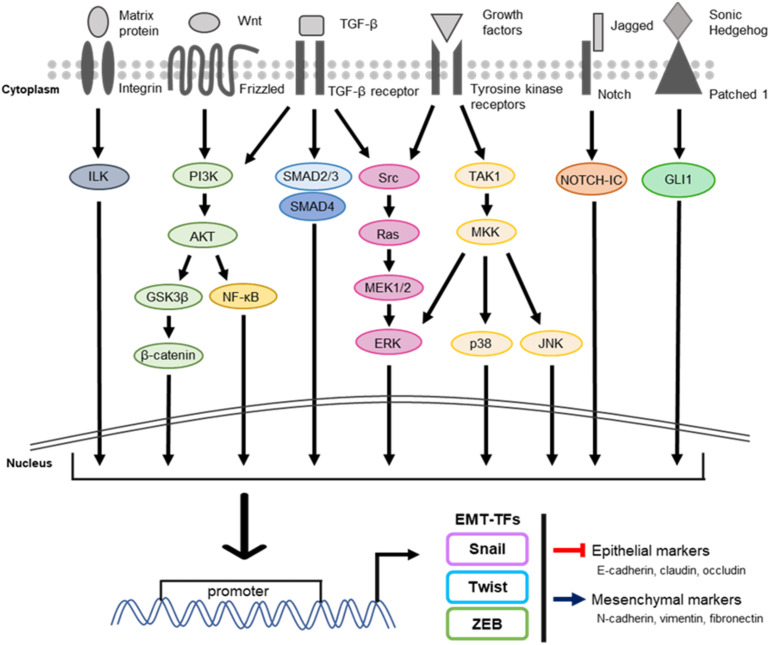
Figure 2.
The common signaling pathways regulating EMT. The progression of EMT is controlled by several extracellular and intracellular signaling pathways. Their coordinated interactions bind to DNA promoter regions of EMT-TFs, leading to promotion of transcriptional activity of EMT-TFs. The expressions of EMT-TFs play a key role in regulating the expression of their target genes related to EMT and cancer metastasis. (Left to right: matrix protein/ILK, WNT/PI3K/β-catenin, TGF-β/PI3K/NF-κB, TGF-β/SMAD complex, growth factors or TGF-β/RAS/ERK, growth factors/TAK1/MAPK, Jagged/NOTCH-ICD, and Sonic Hedgehog/GLI1) ILK, integrin-linked kinase; TGF-β, transforming growth factor-beta; PI3K, phosphoinositide 3-kinase; NF-κB, nuclear factor-kappa B; ERK, extracellular signal-regulated kinase; JNK, c-Jun N-terminal kinases; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; TAK1, transforming growth factor β-activated kinase 1; MEK, MAPK/ERK kinase; MKK, mitogen-activated protein kinase kinase.