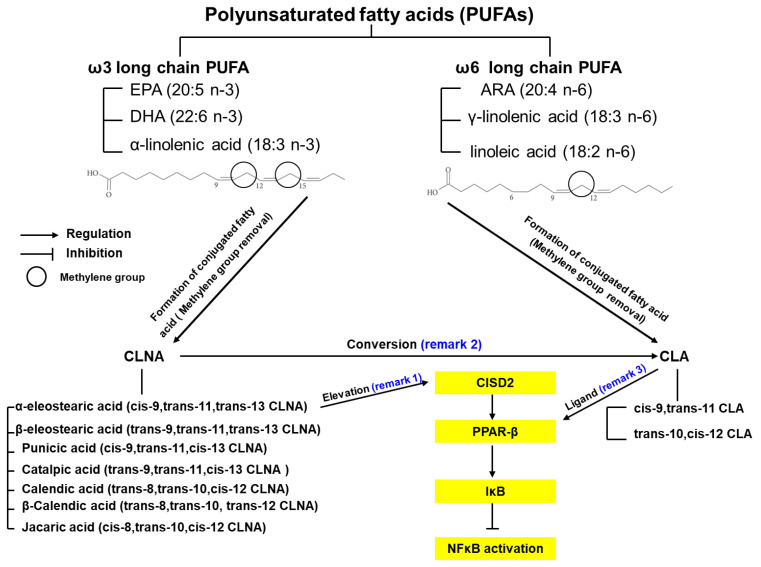
Figure 2.
α-ESA, a conjugated linolenic acid (CLNA) isomer, exerts CISD2-elevating effect. Polyunsaturated fatty acids (PUFAs) are mainly divided into two categories, ω-3 and ω-6. Linoleic acid and α-linolenic acid represent the most fatty acids in the ω-6 and ω-3 fatty acids, respectively. By removing the methylene group (represented as a circle) between double bonds in linoleic acid (left sided chemical structure) and α-linolenic acid (right sided chemical structure), conjugated linoleic acid (CLA) and CLNA isomers are derived. As a phytochemical of wild bitter melon (WBM), α-ESA is a CLNA isomer, which can elevate expression levels of CISD2 (indicated as remark 1). CISD2 serves as a PPAR-β regulator at upstream level. α-ESA can be converted to CLA (indicated as remark 2). CLA has been demonstrated to function as PPAR-β ligand (indicated as remark 3). As a result, α-ESA-driven CISD2 activation induces PPAR-β upregulation, causing the inhibition of IκB degradation and NF-κB activation.