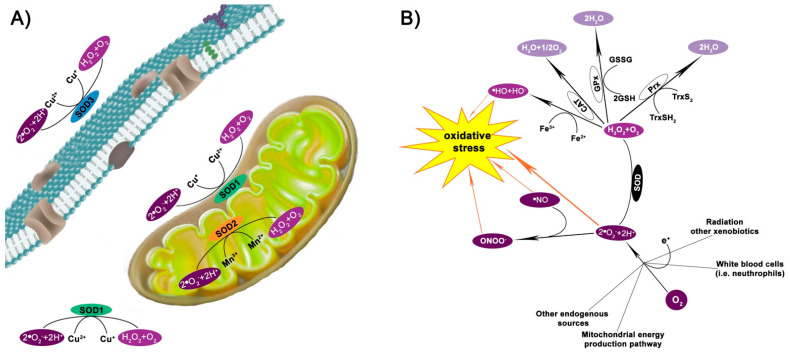
Figure 1.
Superoxide dismutase enzymes. (A) Superoxide dismutases (SODs) are metalloenzymes constitutively expressed in eukaryotes: SOD1 is a Cu, Zn-SOD and is present in the cytosol and the mitochondrial intermembrane; SOD2 is a Mn-SOD localized in the matrix and inner membrane of mitochondria; SOD3 is a Cu, Zn-SOD expressed in the extracellular compartment. Nevertheless, all three forms catalyze the conversion of the superoxide anion free radical (•O2−) into hydrogen peroxide (H2O2). (B) In detail, SOD converts the •O2−, generated in several cellular insults/metabolism, into H2O2 and molecular oxygen (O2). The resulting H2O2 may undergo reduction to water via catalase (CAT), glutathione peroxidases (GPx), or thioredoxin (Trx)-dependent peroxiredoxin (Prx). Otherwise, H2O2 originates •OH via the Fenton reaction in the presence of Fe2+. •O2− may also react with •NO originating the oxidant and nitrating agent peroxynitrite (ONOO−), which further contributes to oxidative-stress damage. GSH = glutathione; GSSG = glutathione disulfide; TrxSH2 = reduced thioredoxin; TrxS2 = oxidized thioredoxin.