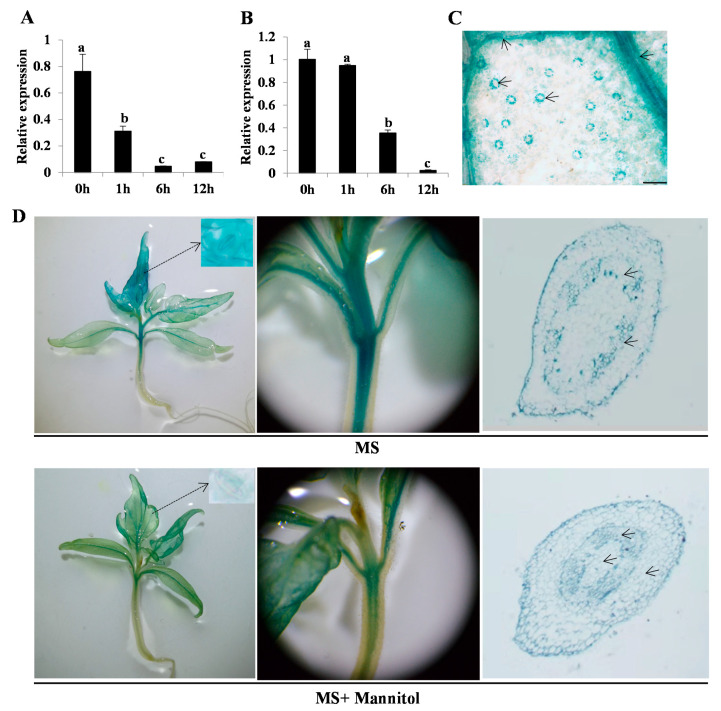
Figure 1.
Expression pattern of SlARF4. Results of quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction (qRT-PCR) analysis showing that SlARF4 expression is reduced by (A) water deficit and (B) abscisic acid (ABA) treatment. Four-week-old tomato seedlings were treated with 100 μM ABA or by desiccation for different durations; whole seedlings were used for RNA extraction. Polyubiquitin (UBQ) (Solyc01g056940) was used as an internal standard. Data was means ± standard error (SE) of three independent biological replicates. Different letters (a, b, c) presented significant difference at level set p < 0.05; (C) Detection of SlARF4 promoter activity in tomato leaves by histochemical GUS staining. (D) Detection of SlARF4 promoter activity in tomato seedlings under normal and water stress conditions. Two-week-old seedlings harboring the pARF4::GUS transgene grown in MS and MS plus mannitol media were subjected to GUS staining. Aboveground part of aseptically cultured pARF4::GUS seedlings grown for 3 weeks (left); enlarged view of the middle and upper part of the stem (center), paraffin section of the stem observed microscopically at 10 (right). Black arrow indicates the stomata and xylem. MS medium; MS + 100 μM mannitol medium. The dot arrows indicates the stomata.