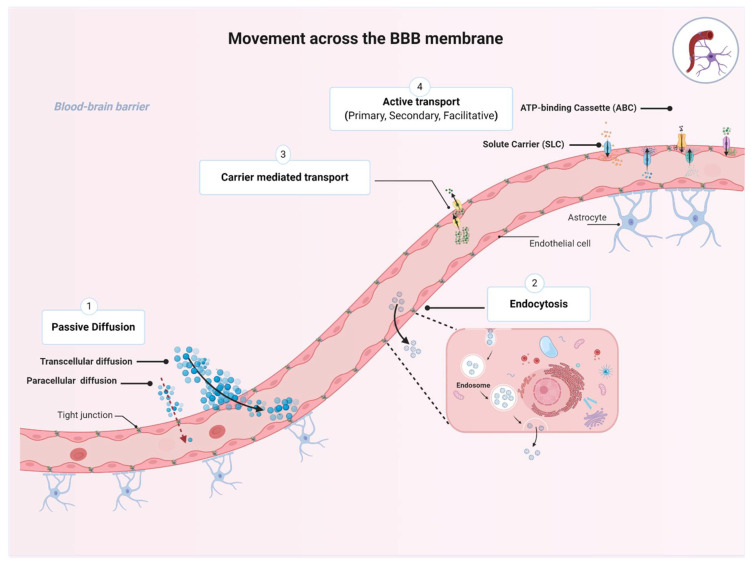
Figure 2.
Transport pathways across the blood–brain barrier (BBB). The passage of various molecules through the brain implies four basic mechanisms allowing specific molecules to move across the BBB membrane including: (1) the passive diffusion (spontaneous movement across a concentration gradient), (2) endocytosis (receptor-mediated, adsorptive, or bulk-phase endocytosis), (3) carrier-mediated transport (movement across a concentration gradient and energy independent), and (4) active transport (movement of molecules against a concentration gradient and energy dependent). Collectively, the four mechanism plays an essential role for maintaining brain homeostasis. (Created with BioRender, accessed on 27 January 2021).