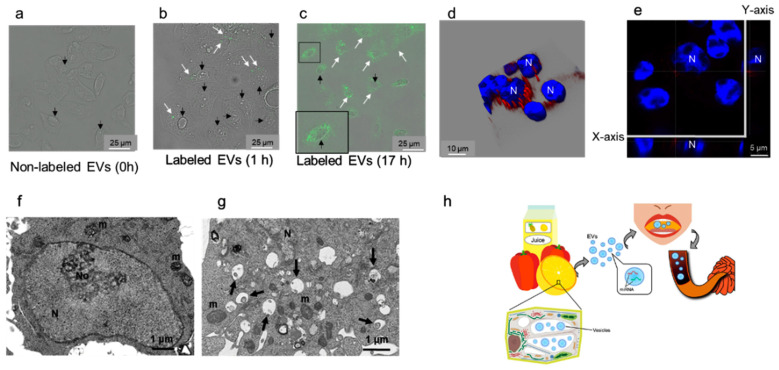
Figure 3.
Plant extracellular vesicle (EV) uptake by intestinal epithelial cells (IEC6) and summary of the main findings of the current study. (a–e) Confocal laser scanning microscopy analysis of IEC6 cell interaction with plant EVs. (a) IEC6 cells exposed to unlabeled EVs for control (0 h). IEC6 cells after 1 h (b) and 17 h (c) of exposure to EVs labeled with PKH67 (green). White arrows: EVs labeled with PKH67 taken up by IEC6 cells. Black arrows: nuclei of IEC cells are shown with differential interference contrast (DIC). The inset in c shows an enlarged boxed area. Bar = 25 μm. IEC6 cells after 17 h (d,e) of exposure to EVs labeled with PKH26 (red). N, nucleus stained with 4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (blue). A three-dimensional composite image of Z-sections of IEC6 cells (d) and one Z-section from (d) with the X and Y sections indicated (e) are shown. Perinuclear localization of labeled EVs is apparent. (f,g) Transmission electron microscopy analysis of IEC6 cell interaction with plant EVs. (f) IEC6 cells were exposed to phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) instead of EVs. (g) IEC6 cells after 17 h of exposure to EVs. Endosomes and phagosomes (black arrows) are localized in the perinuclear region. N, nucleus; No, nucleolus; m, mitochondria. (h) Overview of the implications of the findings of the current study. Extracellular vesicles are present in the multivesicular bodies (MVBs) and central vesicles in plant epidermal cells. Juices squeezed from edible plants and 100% natural edible plant juice available on the market contain EVs that correspond to exosome-like nanovesicles. These nanovesicles contain microRNAs (miRNAs). When humans drink juice, miRNAs (packed in EVs to protect them from degradation) pass through the gastrointestinal tract and are absorbed by small intestine enterocytes.