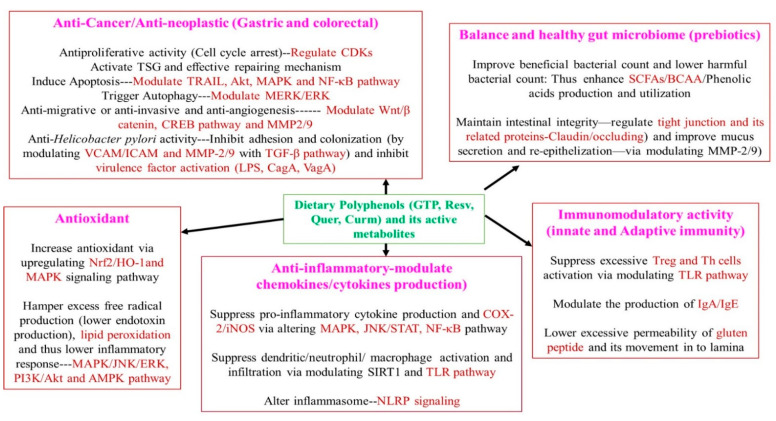
Figure 4.
Brief description of the underlying gastroprotective mechanism of dietary polyphenols. GTP—green tea polyphenol, Curm—Curcumin, Resv—Resveratrol, Quer—Quercetin, Nrf2—Nuclear factor-E2-related factor, HO-1—Heme Oxygenase-1, NF-κB—Nuclear factor Kappa B, SIRT—Sirtuin, MAPK—Mitogen-activated protein kinase, JNK—c-Jun N-terminal Kinase, PI3K/Akt—Phosphatidylinositol-3-kinase/Protein kinase B, ERK—extracellular signal-regulated kinase, JNK—c-Jun N-terminal kinase, STAT—signal transducers and activators of transcription, JAK—Janus kinase, AMPK—Adenosine monophosphate-activated protein kinase, TLR—Toll-like receptor, NLRP—Nod-like receptor protein, CREB—cAMP response element-binding, Wnt—Wingless-related integration site, CDKs—Cyclin-dependent kinases, MMP—Matrix metalloproteinase, VCAM—Vascular cell adhesion molecule, ICAM—Intracellular adhesion molecule, BCAA—Branched-chain amino acids, SCFAs—Short-chain fatty acids, Treg—Regulatory T cells, Th—Helper T cells.