Figure 2.
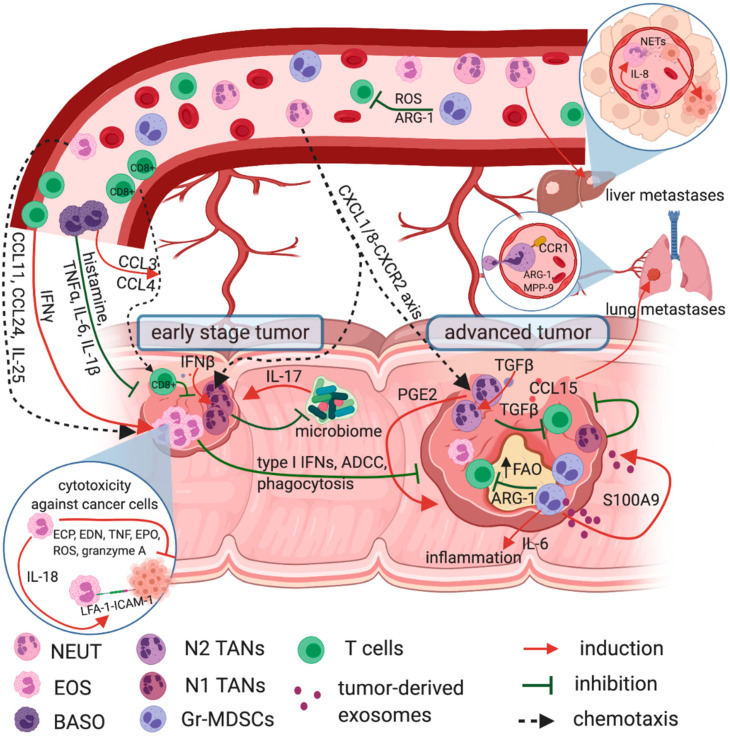
Granulocytes role in CRC. Eosinophils have an anti-tumor role in CRC and their infiltration into the tumor is considered as a positive prognostic marker. They are recruited to the tumor site by CCL11, CCL24, and IL-25 where they are activated by IFNγ to secrete ECP, EDN, EPO, TNF, granzyme A, and produce ROS, all with direct cytotoxicity against cancer cells. Tumoricidal effect of eosinophils depends on cell-to-cell contact and IL-18, which in the autocrine loop enhances the LFA-1—ICAM-1 mediated eosinophil adhesion to the target cells. Basophils are also beneficial in CRC and their role is related to the secretion of the granules content, including histamine and proinflammatory cytokines—e.g., TNFα, Il-6, IL-1β—augmenting inflammatory reaction, recruiting cancer-specific CD8+ T cells (CCL3 and CCL4) into the tumor and enhancing cancer cell apoptosis. Neutrophils possess both anti-tumor and pro-tumorigenic activities. Under the influence of CXCL8 (IL-8) they are recruited from peripheral blood to the tumor site and prompted for NETs formation, which support tumor spread and liver metastasis. Additionally, neutrophils are recruited into the tumor by CCL15-CCR1 pathway, where CCR1+ TANs with ARG-1 and MMP-9 activity are associated with lung metastasis. In tumors, TANs are involved in local immunosuppression through prostaglandin PGE2 and TGFβ secretion, supporting the tumor growth. Unlike N2, N1 TANs possess anti-tumorigenic functions. Their increased infiltration was shown in the early stage of CRC, where they affect the colon microbiome and hamper IL-17 dependent tumor development. Moreover, activated by type I IFNs N1 TANs inhibit angiogenesis and effectively eliminate tumor cells via antibody dependent cell-mediated cytotoxicity (ADCC) or phagocytosis. Gr-MDSCs are potent inhibitors of T cell proliferation and anti-tumor response. Their mechanisms involve ARG-1 activity, ROS production, an increased fatty acid uptake and activated fatty acid oxidation (FAO). Moreover, Gr-MDSCs produce high amounts of IL-6 for sustained inflammation in colon epithelium, thereby promoting CRC progression. Pro-tumorigenic action of Gr-MDSCs also includes secretion of exosomes containing S100A9, which additionally stimulate the tumor growth.