Figure 2.
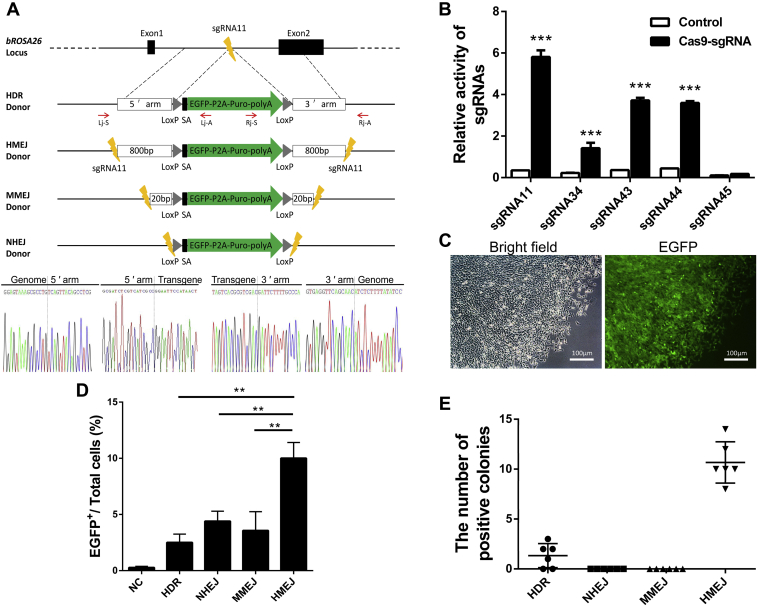
BROSA26 endogenous promoter-driven reporter gene expression in BFFs.A, schematic overview of HDR-, HMEJ-, MMEJ-, and NHEJ-based gene targeting methods at the bROSA26 locus. 5ʹ arm/3ʹ arm, left/right homology arm; lightnings, sgRNA target sites; Lj-S/Lj-A, 5ʹ junction PCR forward/reverse primer; Rj-S/Rj-A, 3ʹ junction PCR forward/reverse primer; Black rectangles, splice acceptor. Gray triangles, LoxP site. Sanger sequencing confirming the precise insertion of the exogenous DNA. B, the activity of sgRNAs was measured by luciferase assay. SSA reporter plasmid, internal reference vector, and Cas9 expression plasmids containing 20-nt guide sequence or not containing (control) were transfected into 293T cells for 48 h. The relative luciferase activity was calculated by standardizing transfection efficiency. C, stably transfected BFFs by the HDR-based method after puromycin selection 10–12 days under a fluorescence microscope. D, comparison of the integration efficiency of the HDR-, HMEJ-, MMEJ-, and NHEJ-based methods. Each of the four types of donors, respectively, with Cas9/sgRNA11 were transfected into BFFs for 7 days, expanded, and subjected to FACS. Nontransfected cells were used for negative controls (NC). E, distribution of different KI patterns by four types of donors. BFFs were transfected with donors and Cas9/sgRNA via electroporation, and then the transfected colonies were counted following 10–12 days of puromycin selection. Positive colonies of the HDR groups (1.333 ± 1.211) and the HMEJ groups (10.67 ± 2.066) were confirmed by 5ʹ and 3ʹ junction PCR and sequence analysis. Data are presented as the mean ± SD of three independent experiments. Student's t-test was used to evaluate the differences. ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.01; ∗∗∗p < 0.001.